Gurugram: The Millennium City
Gurugram, previously known as Gurgaon, is a prominent city situated in the southeastern region of Haryana, India. It is located approximately 30 kilometres southwest of New Delhi and serves as a vital component of the National Capital Region (NCR). The city has transitioned from its agricultural origins to emerge as an industrial and financial centre, commonly referred to as the “Millennium City”.
Gurugram is recognised as one of the largest hubs for information technology and business process outsourcing (BPO) in India. This city serves as the headquarters for numerous multinational corporations operating across various sectors, including finance, technology, and manufacturing. Additionally, Gurugram has emerged as a significant centre for automobile manufacturing, hosting prominent companies such as Maruti Suzuki and Hero MotoCorp.

Over the past few decades, Gurugram has experienced rapid urbanization and industrial growth. The Gurugram Metro Project also known as Rapid Metro is a major initiative aimed at enhancing urban transportation in Gurugram, Haryana. The metro connectivity boosts the infrastructure of the city and effectively links the city with Delhi and other neighbouring regions.

Delhi Metro Yellow Line: The First Expansion into Gurugram
To increase connectivity between Delhi and Gurugram , Delhi Metro Rail Corporation ( DMRC) planned to extend the Yellow Line of Delhi Metro which was operating from Samaypur Badli to Saket.
A 14.47 km extension from Qutab Minar Station to Millenium City Centre ( formerly known as Huda City Centre) covering 10 stations was planned was DMRC. Out of 14. 47 km, the 7.5 km falls in Haryana covering 5 elevated stations while the 7.42 km stretch falls under Delhi.
In 2010, this section finally became operational marking the first metro connectivity in the Gurugram City.
Stations:
| Stations Located in Delhi | Stations located in Haryana |
| Qutab Minar | Guru Dronacharya |
| Chhatarpur | Sikanderpur |
| Sultanpur | MG Road |
| Ghitorni | IFFCO Chowk |
| Arjangarh | Millenium City Centre |

Funding Mechanism of this Section
| Total cost Segment | Cost |
| Delhi Segment | Rs. 734 crore |
| Haryana Segment | Rs 743 crore |
| Total | Rs 1477 crore |
Haryana Segment’s Cost Breakdown (Rs in crore)
| Particulars | GOH | GOI | DMRC | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cost of land | 20 | – | – | 20 |
| Cost of the network (excluding taxes in the ratio of 80:20) | 456 | 1114 | – | 570 |
| Interest-free SD for Central taxes to be shared between GOH & GOI in the ratio of 20:80 | 11 | 44 | – | 55 |
| State Taxes | Exempted by GoH | – | – | – |
| Cost of rolling stock | – | – | 98 | 98 |
| Total | 487 | 158 | 98 | 743 |
Delhi Segment’s Cost Breakdown (Rs in crore)
| Particulars | Amount |
| Cost Of Construction | 734 Crore |
| Land Cost | 49 Crore (Shared by GNCTD and GoI as subordinate debt) |
| Main Debt | 352 Crore |
| Equity by GNCTD/GoI | 333.00 Crore |

Rapid Metro: The Feeder Connection
Overview
Gurugram Metro, also known as Rapid Metro, is a Light Rail Transit System (LRTS) and consists of one corridor spanning 12.1 km from Moulsari Avenue (Cybercity) to Sector 55-56. The first corridor of the Rapid Metro was developed into 2 Phases.
In Phase 1 of the project, a 5.1-kilometre line was constructed to connect the Delhi Metro’s Sikanderpur Station, situated on the Yellow Line, with the DLF Cybercity business district. This line commenced public commercial operations on November 14, 2013.
In Phase 2 of the project, a 7-kilometer extension of the line was inaugurated on March 31, 2017. This extension linked Sikanderpur Station to Sector 55-56 via five new stations along Golf Course Road.

Historical Background of Rapid Metro
- The Rapid Metro was initially developed and operated by Rapid MetroRail Gurgaon Limited (RMGL) and Rapid MetroRail Gurgaon South Limited (RMSGL), both of which acted as the subsidiaries of Infrastructure Leasing & Financial Services (IL&FS).
- This project is distinguished as the world’s first fully privately financed modern light metro system, without any financial contribution from the Union Government, the Government of Haryana, or any public sector enterprise.
- However, RMRG started facing financial crises and was unable to run operations due to low footfall and financial challenges.
- To ensure effective operations the Delhi Metro Rail Corporation (DMRC) took over the operations on 22 October 2019.
Incorporation of HMRTC and GMRL
The Haryana Mass Rapid Transport Corporation Limited (HMRTC) was incorporated on 24 March 2012 as a special-purpose vehicle (SPV) to plan and implement mass rapid transit systems in Haryana, including Gurugram.
The Gurugram Metro Rail Limited (GMRL) was incorporated on 9 February 2024 as a joint venture between the Government of India (GoI) and the Government of Haryana (GoH) to implement the new metro corridor in Gurugram.
Key Specification
| Speed and Track | Top Speed: 80 kmphAverage Speed: 35 kmphTrack Gauge: Standard Gauge – 1435 mm |
| Electrification | 750 V DC Third Rail |
| Signalling | Cab Signalling/Distance to Go |
| Rolling Stock | 36 coaches (12 train sets x 3) |
Gurugram Metro Route Details
| Operational | 12.1 km |
| Approved | 28.8 km |
| Under Construction | 0 km |
| Proposed | 170.19 km |
Operational Route
Line-1: Moulsari Avenue (Cybercity) – Sector 55-56
- Length: 12.1 km
- Type: Elevated
- Depot: Sector 24 and Sector 54
- Number of Stations: 11
- Station Names (Built Phase 1): Sikanderpur, DLF Phase 2, Vodafone Belvedere Towers, IndusInd Bank Cyber City, Micromax Moulsari Avenue, DLF Phase 3
- Station Names (Built-in Phase 2): Phase 2 Stations (5): DLF Phase 1, Sector 42-43, Sector 53-54, Sector 54 Chowk and Sector 55-56

Gurugram Metro Approved Routes
Overview
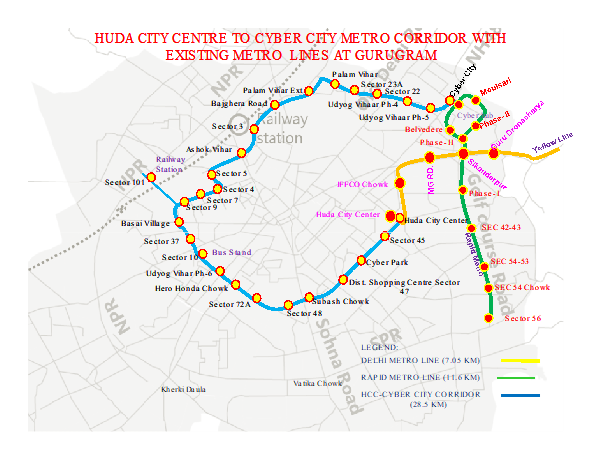
To link the old Gurugram with the new Gurugram and enhance metro connectivity, a new corridor spanning 28.8 km from Huda City Centre to Cyber City with a spur to Dwarka Expressway has been under implementation. This section will feature 27 stations.
The total completion cost of the project will be Rs.5,452 crore. Additionally, the route will have a spur from Basai village that will provide connectivity to the depot.
| Corridor Name | Length (in KM) | No. of Stations | Type |
| Huda City Centre to Cyber City – Main Corridor | 26.65 | 26 | Elevated |
| Basai Village to Dwarka Expressway – Spur | 1.85 | 1 | Elevated |
| Total | 28.5 | 27 | Elevated |
Key Approvals & DPR
- The DPR of this routes was prepared by a consortium of RITES and the School of Planning and Architecture (SPA).
- HMRTC’s board of directors approved this route in December 2019.
- This new metro corridor received approval from the Haryana state government’s cabinet in August 2020.
- The Union Cabinet, chaired by the Hon’ble Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi approved this new corridor on 7 June 2023.
Key Specifications
| Speed and Track | Design Speed: 80 kmphAverage Speed: 34 kmphTrack Gauge: Standard Gauge – 1435 mm |
| Proposed Completion Cost | Rs.5,452 crore. |
| Completion Time | 4 years from the date of Sanction of the project |
| Implementing Agency | Haryana Mass Rapid Transport Corporation Ltd. (HMRTC) |
Funding Mechanism
Proposed Completion cost: Rs.5,452 crore.
| GoI share | Rs. 896.19 cr |
| GoH share | Rs. 1,432.49 cr |
| Local Bodies Contribution (HUDA) | Rs. 300 cr |
| PTA (Pass through Assistance- Loan component) | Rs. 2,688.57 cr |
| PPP (Lift & Escalator) | Rs. 135.47 cr |
Additionally, the project will receive financial assistance from the European Investment Board (EIB) and the World Bank (WB).
Estimated Ridership
| Year | Estimated Ridership |
| Year 2026 | 5.34 Lakhs |
| Year 2031 | 7.26 Lakhs |
| Year 2041 | 8.81 Lakhs |
| Year 2051 | 10.70 Lakhs |
Recent Update on this Route
Gurugram Metro Rail Limited (GMRL) has recently issued a tender valued at INR 1286 Crores for the construction of the initial segment of this new Gurugram Metro Line.The contract entails the construction of a 15.221-kilometer metro rail viaduct, accompanied by 14 elevated stations, which will connect the Millennium City Centre to Sector 9.
Announcement of 2 new Corridors
In order to bridge the longstanding gap between the old Gurugram and the developing Gurugram, HMRTC has recently issued a tender for the development of a Detailed Project Report (DPR) for two new metro corridors.
Route Details
| Corridor | Length | Key Stops | Major Intersections/Interchanges |
| Corridor 1 | 17 km | Vatika Chowk, Subhash Chowk, Rajiv Chowk, Sohna Chowk, Sector 4-7 Chowk, Railway Road | Millennium City Centre-Cyber City line at Subhash Chowk and Sector 5 stations, Rapid Rail Corridor interchange at Rajiv Chowk |
| Corridor 2 | 13.6 km | Golf Course Extension Road, Hong Kong Market (Sector 57), Ardee City, Millennium City Centre, Signature Tower, Maharana Pratap Chowk, Atul Kataria Chowk, Sheetla Mata Road | —- |
Impacts of New Metro Route in Gurugram
1. Enhanced Connectivity: The expansion of the Gurugram Metro will improve the urban mobility of the Millennium City by linking major business hubs and residential zones. This connectivity will enable residents and professionals to commute more efficiently to their offices, reducing travel time and enhancing accessibility across the city.
2. Reduced Traffic Congestion: Due to rapid urbanisation the city started witnessing major traffic congestion on the roads. The metro system provided the residents with a more convenient, fast and effective mode of public transportation and reduced the dependency of the residents on private vehicles, thereby alleviating the traffic on the roads. The upcoming metro corridor will further help the city to lower its carbon footprint.
3. Economic Growth: The city serves as a major commercial and business hub in Delhi. The establishment of a new metro system in Gurugram will generate more employment opportunities in the city which will result in increasing economic growth of the city. Furthermore, the metro system will also result in infrastructure development of the city and attract more business setups and investments in the city thereby boosting local economies.
4.The Multi-Modal Hub: The route is designed to feature an interchange facility that integrates various modes of transportation, including a railway station located near Sector 5. Furthermore, this corridor will intersect with the forthcoming Regional Rapid Transit System (RRTS) route at Sector 22, as well as connect to the existing Millennium City Centre Station of the Delhi Metro’s Yellow Line.
Conclusion:
The expansion of the metro system in Gurugram is integral to enhancing urban mobility and connectivity within the city and the National Capital Region (NCR). The new corridors in Gurugram will provide unified access between its residential, commercial, and industrial areas. With its connection to the Delhi Metro and the addition of new corridors, the city hopes to tackle the increasing need for integrated public transport, less congestion on the roads, and eco-friendly movement. To maximize the utilization of infrastructure, it is essential for the authorities to facilitate key components such as accessibility, last-mile connectivity, and affordability. These measures will contribute to achieving the anticipated footfall and ensuring the financial sustainability of the project. As Gurugram evolves as a global business center, its metro infrastructure will be key to its future as a smart and sustainable city.








