A Quick Tour of Hyderabad
Hyderabad, the capital of Telangana, occupies 650 square kilometres of space in the Deccan Plateau. Known as the ‘city of Nizams’, Hyderabad is known for its rich cultural heritage, blending unique cultures with a touch of modernity. Celebrating a mix of religions, the Hyderabadi people celebrate every occasion with a north-south mix.
With a population of around 11,068,877, Hyderabad is the fourth most populous city in India. The city is well-known for its artistic work such as Golconda and Hyderabad painting styles which are branches of Deccani painting.
Showcasing the blend of culture, Hyderabad is one of the most visited cities due to its culture, cuisines, and educational hubs. It is an important learning centre in South India. Hyderabad metro is a saviour for locals and tourists to travel around and explore the city.
The Beginning of Metro in Hyderabad

Hyderabad is one of the most loved cities in India. Due to the rising population and tourists in the city, there was a pressing need for a transport system which led to the rise of Hyderabad Metro.
As Hyderabad’s population continued to rise, the state government of Telangana, in partnership with South Central Railway, introduced the Multi-Modal Transport System (MMTS) to address the growing demand for public transportation. Despite plans for MMTS Phase 2, the city’s rapid growth soon exceeded the system’s capacity. Recognising the need for a more comprehensive solution, the Union government approved the Hyderabad Metro Rail project in 2003.
Overview of Hyderabad Metro
Initially established under the Andhra Pradesh Municipal Tramways Act of 2008, the project was later brought under the Central Metro Act. This transition allowed for adjustments in fare structures and operational regulations.
Unique Features of Hyderabad Metro
- After the Delhi Metro and Namma Metro, the Hyderabad Metro is the third longest operational metro network in India.
- Hyderabad Metro is recognized as the world’s largest elevated metro rail system. The Hyderabad Metro is based on the DBFOT model, that is, Design, Build, Finance, Operate, and Transfer.
Planning and DPR of Hyderabad Metro
The Delhi Metro Rail Corporation (DMRC) was tasked with surveying the proposed lines for the Hyderabad Metro and preparing the Detailed Project Report (DPR). This comprehensive report included an assessment of feasibility, technical specifications, and financial projections, which laid the groundwork for the project’s development.
Funding and Construction of Phase 1
The estimated cost of the Hyderabad Metro Phase 1 is Rs. 18,800 crore. In 2007, the central government approved Rs. 1,639 crore as monetary aid through the Viability Gap Funding Project. In April 2012, the construction of Hyderabad Metro’s Phase 1 was started by L&T Metro Rail Hyderabad Limited. L&T Metro Rail Hyderabad Limited was established by the construction company Larsen & Toubro to develop the Hyderabad Metro Project.
Hyderabad Metro Project Underway
Phase 1 of Hyderabad Metro was scheduled to be fully operational by December 2015, however, the construction ended in February 2020. Phase 2 of Hyderabad Metro is currently in the proposal stage.
Bidding and Financials for Hyderabad Metro
In July 2008, the bidding process for the Hyderabad Metro concluded, and Maytas won the contract. However, by March 2009, Maytas failed to secure financial closure, leading the state government to cancel the project.
During the rebidding process in July 2010, Larsen & Toubro (L&T) won the project with the lowest bid of Rs. 121.32 billion. Against the approved funds of Rs. 48.53 billion, L&T offered to take on work for around Rs. 14.58 billion as viability gap funding.
The Hyderabad Metro project eventually received full financing from a consortium of 10 banks led by the State Bank of India. At the time, this arrangement represented the largest funding for a public-private partnership project in India, excluding power infrastructure.
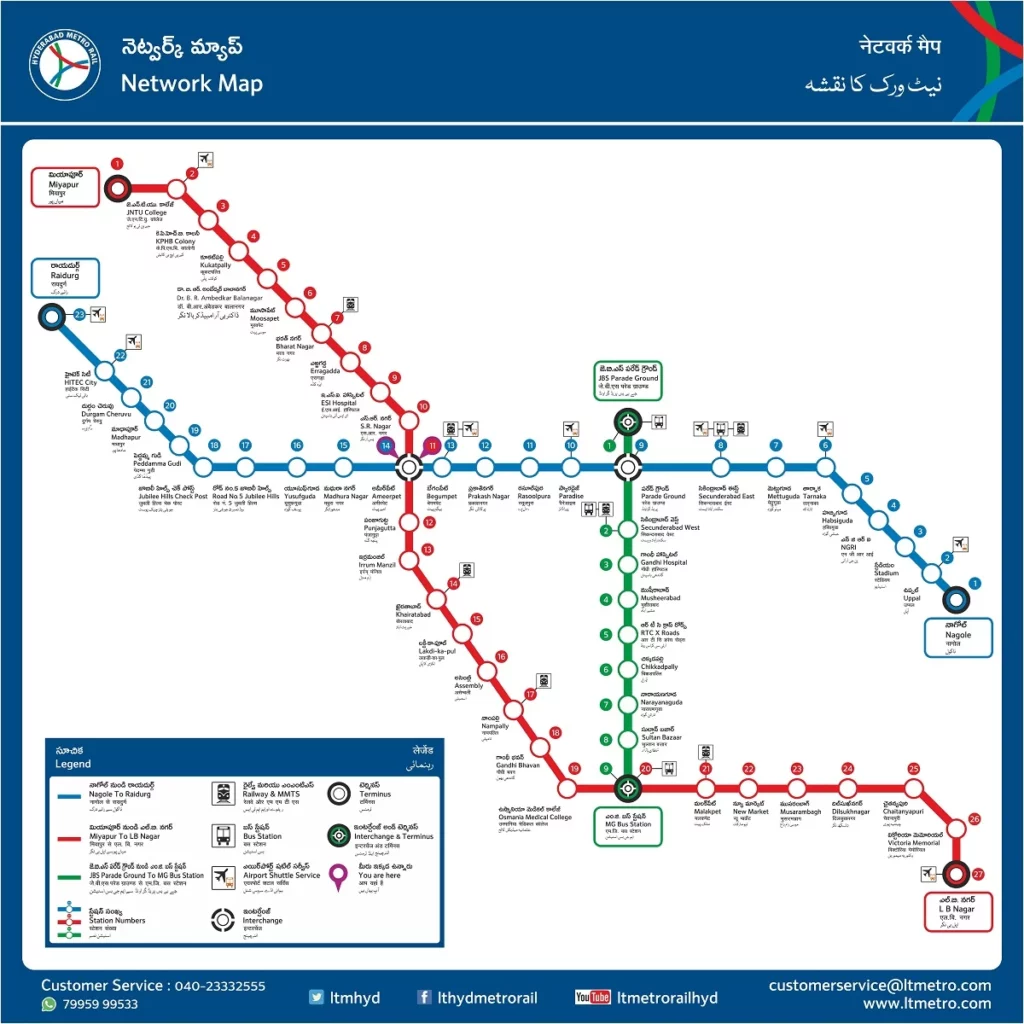
Lines of Hyderabad Metro
| Operational: 67 km | Under Construction: 0 km | Approved but Unbuilt (Phase 1): 5 km | Proposed (Phase 2): 70 km Estimated Cost of the Operational Project: Rs. 18,800 crore |
Hyderabad Metro’s Operational Lines
Phase 1 (67 km)
- Line 1 (Red Line): Miyapur – L B Nagar
- Distance: 29.21 km
- Stations: 27
- Status: Operational since 2017
| Elevated Stations (23) | Underground Stations (4) |
| Miyapur, JNTU College, KPHB Colony, Kukatpally, Balanagar, Moosapet, Bharatnagar, Erragadda, ESI Hospital, SR Nagar, Lakdikapul, Assembly, Nampally, Gandhi Bhavan, Osmania Medical College, MG Bus Station, Malakpet, New Market, Musarambagh, Dilsukhnagar, Chaitanyapuri, Victoria Memorial, L B Nagar | Ameerpet, Punjagutta, Irrum Manzil, Khairatabad |
- Line 2 (Green Line): JBS Parade Ground – MGBS
- Distance: 15 km
- Stations: 16
- Status: Operational since February 2020
| Elevated Stations (16) |
| JBS Parade Ground, Parade Ground, Secunderabad West, Gandhi Hospital, Musheerabad, R.T.C. Cross Roads, Chikkadpally, Narayanguda, Sultan Bazar, M.G. Bus Station, Salarjung Museum, Charminar, Shah-Ali-Banda, Shamsherganj, Jungametta, Falaknuma |
- Line 3 (Blue Line): Raidurg – Nagole
- Distance: 27 km
- Stations: 23
- Status: Operational since November 2017
| Elevated Stations (23) |
| Raidurg, HITECH City, Durgam Cheruvu, Madhapur, Peddamma Gudi, Jubilee Hills Check Post, Road No 5 Jubilee Hills, Yousufguda, Taruni Madhura Nagar, Ameerpet, Begumpet, Prakash Nagar, Rasoolpura, Paradise, Parade Ground, Secunderabad East, Mettuguda, Tarnaka, Habsiguda, NGRI, Stadium, Uppal, Nagole |
Hyderabad Metro’s Proposed Lines
Phase 2
The plan of Phase 2 of Hyderabad Metro is currently in the proposal stage. The DPR of the Phase 2 Hyderabad Metro was prepared by Delhi Metro Rail Corporation Limited and submitted to the Telangana Government in February 2020. The DPR was finalized in January 2024 by Telangana Chief Minister.
The construction of Hyderabad Metro’s Phase 2 is solely handled by the state government of Telangana. Hyderabad Metro’s Phase 2 will include 6 elevated corridors. These corridors will be the extensions of the existing lines of Phase 1.
| Distance: 70 kmEstimated Cost: Rs. 17,150 croreEstimated Completion: 2030 |
| Red Line Extension | Miyapur – BHEL – Patancheruvu | Distance: 14 km |
| Red Line Extension | LB Nagar – Vanasthalipuram – Hayathnagar | Distance: 8 km |
| Green Line Extension | MGBS – Old City – Falaknuma – Chandrayangutta X Road | Distance: 7 km |
| Blue Line Extension | Nagole – LB Nagar – Chandrayangutta X Road – Mallardevpally Jct – Shamshabad Airport | Distance: 29 km Estimated Cost: Rs. 6,250 crore |
| Blue Line Extension | Raidurg – Biodiversity Junction – Nanakramguda Junction – Wipro Junction – American Consulate (Financial District) | Distance: 8 km |
| Spur Line of Blue Line’s Extension | Mallardevpally – Aramgarh – New High Court at Rajendra Nagar | Distance: 4 km |
| With a length of 70 km, the Detailed Project Report (DPR) of Phase 2 is ready. It will be put in the state cabinet for approval and later on to the Central government for sanctioning of funds. |
Airport Metro Express Line
Also known as Corridor IV, the Hyderabad Airport Metro Express Line is a proposed semi-high-speed rail line that is planned to connect Mindspace Junction and Rajiv Gandhi International Airport in Shamshabad via 10 stations. The DPR of the Airport Metro Express Line is prepared by the Delhi Metro Rail Corporation (DMRC).
It is a 31 km Line that will be funded by the Telangana Government and executed by HAML (Hyderabad Airport Metro Ltd).
| The Airport Metro Express Line was scrapped in 2024 but currently, it has again received a green light. |
- Type: Elevated (28.5 km) and Underground (2.5 km)
- Estimated Cost: Rs. 6,250 crore
- Stations (10): Mindspace, Raidurg, Biodiversity, Nanakramguda, Narasingi, TSPA Junction, Rajender Nagar, Shamshabad Junction, Airport Cargo and RGIA Terminal (only underground station)
| 2022 | December 9 | The foundation stone of the Hyderabad Metro Airport Express line was laid by the Chief Minister of Telangana. |
| 2023 | April | SYSTRA – RITES – DB Engineering JV declared as the preferred bidder for the contract of General Consultant. |
| July | Larsen & Toubro was declared as the lowest bidder of civil construction and system procurement of the Airport Express Line. |
Hyderabad Metro Project’s Timeline
| Date | Line | Distance | |
| 2017 | November 29 | Nagole – Ameerpet (Blue Line) | 17.60 km |
| November 29 | Miyapur – Ameerpet (Red Line) | 12.20 km | |
| 2018 | September 24 | Ameerpet – LB Nagar (Red Line) | 16 km |
| 2019 | March 20 | Ameerpet – HITEC City (Blue Line) | 8.5 km |
| November 29 | HITEC City – Raidurg (Blue Line) | 1.5 km | |
| 2020 | February 7 | JBS Parade Ground – MGBS (Green Line) | 11 km |
Contractors List
| Contractor Name | Contract Details |
| Larsen & Toubro | 90% |
| The Government of Telangana | 10% |
Key Specifications of Hyderabad Metro
| Speed and Track | Maximum Speed: 80 km/h |
| Average Speed: 35 km/h | |
| Track Gauge: Standard Gauge Track measuring 1435 mm | |
| Safety and Electrification | Electrification: The metro is powered by a 25 kV, 50 Hz AC overhead catenary (OHE). |
| Signalling: The metro’s signalling system will be based on Communication-based Train Control (CBTC). | |
| Rolling Stock | 171 coaches (57 train set x 3)Hyundai Rotem |
| Daily Ridership | As of July 2024, the daily ridership of Hyderabad metro is 5,36,000. |
Budget 2024 Updates
| The Hyderabad Old City metro project has received an allocation of Rs. 500 crore in the State Budget announced by the Telangana government. The state government has also announced an allocation of Rs. 100 crore for the metro extension to the Airport. |
Challenges Faced by Hyderabad Metro
1.Engineering Challenges
Engineers of Hyderabad Airport Metro are facing technical difficulties in the alignment of the airport metro. There are issues as the station falls on the critical stretch from Raidurg to Nanakramguda station. Engineers had to undergo a deep study to understand the route’s area that is, flyovers, underpasses, and high-rise buildings.
2. Poor Frequency
The Green line faces frequency issues. The daily ridership of the Green Line is around 25,000 passengers, while that of the Blue Line is 32,000 passengers. The green line experiences lower frequency due to the time frame of 13 to 20 minutes between metros.
Benefits of Hyderabad Metro
1.Reduced Road Congestion
Metro is considered as an efficient public transport. It is the best alternative to reduce traffic on the road as people prefer the metro for mobility due to convenience. Due to the Hyderabad Metro, more people travel easily to avoid traffic and reach their destination on time.
2.Economic Growth
Metro has helped to raise the GDP of the city. With the metro as a transport facility, many people migrated to the city due to education and job opportunities. With the rise in the metro, there is also a rise in educational institutions, healthcare centres, and job opportunities for both individuals and businesses.
3.Impact on Real Estate
The residents and businesses have benefited the most from the construction of the metro in the city. There is a significant rise in property values, mostly in the areas having access to the metro.
Conclusion
The Hyderabad Metro has significantly contributed to the city’s infrastructure. It offers a reliable, fast, and eco-friendly mode of transportation while addressing the needs of a rising population. The metro project supports the city’s ambitious growth plans. As new phases and extensions are on the way, including the links to the airport and other critical areas, the metro system will continue to play a crucial role in enhancing connectivity, reducing travel times, and supporting sustainable urban development.
With the commitment to improve its service and expand its reach, the Hyderabad Metro is a cornerstone of the city’s transit network, driving its economic and social progress into the future.








