A Quick Tour of Delhi
Delhi, the National Capital Territory of India, has been a union territory since November 1, 1956, and spans 1,484 square kilometres. With a population exceeding 11 million, it is a major urban centre surrounded by satellite cities like Ghaziabad, Faridabad, Gurgaon, Noida, Greater Noida, and YIEDA City, forming a metropolitan region with over 28 million inhabitants.
Known for its historical significance, diverse infrastructure, and vibrant economy, Delhi is a hub for finance, IT, public administration, and social services. The city’s extensive network of highways, railways, and metro systems ensures efficient connectivity for its large population.
The Beginning of Delhi Metro
1969 Study
The study of 1969 traffic and travel characteristics led to the idea of a mass rapid transit system for Delhi. Over the years, various government-commissioned committees evaluated technology, route alignment, and legal frameworks. In 1984, the Urban Art Commission proposed a multimodal transport system.
Between 1981 and 1998, Delhi’s population doubled, and vehicle numbers increased fivefold, leading to severe traffic congestion and pollution. Efforts to privatise buses in 1992 failed, worsening public transport conditions.
Overview of Delhi Metro
On May 3, 1995, the Delhi Metro Rail Corporation (DMRC) was established by the Government of India under Prime Minister H.D. Deve Gowda, with Elattuvalapil Sreedharan as its first managing director. The DMRC is a joint venture between the Government of India and the Government of Delhi, under the administrative control of the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs (MoHUA).
On December 31, 2011, Mangu Singh succeeded Sreedharan as managing director.
Delhi Metro Authorization
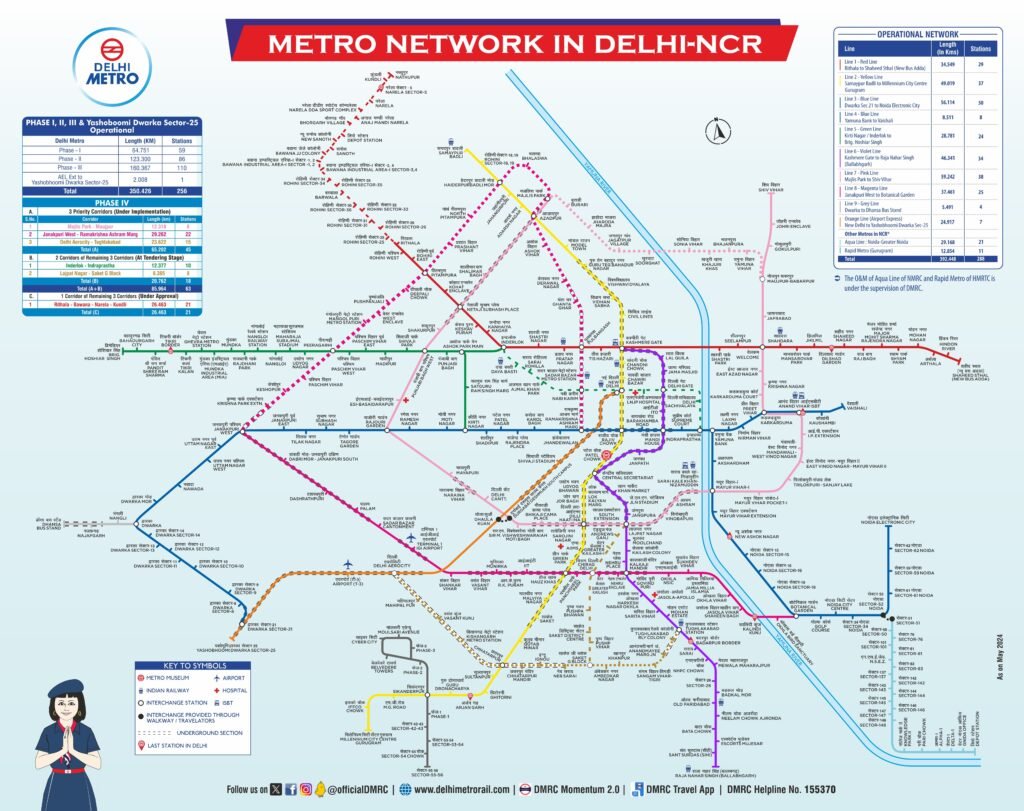
The Delhi Metro Rail Corporation (DMRC) is a joint venture between the Government of India and the Government of Delhi. It is under the administrative control of the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs (MoHUA). It operates 10 colour-coded lines, covering 256 stations over a network of 350.42 kilometres. As India’s largest and busiest metro system, it plays a crucial role in urban mobility and connectivity. Additionally, Delhi Metro is the second-oldest metro system in India, following the Kolkata Metro.
Key Specifications of Delhi Metro
| Speed and Track | Maximum Speed: 80 km/h |
| Average Speed: 34 km/h | |
| Track Gauge: Broad Gauge: 1676 mm (Lines 1-4) and Standard Gauge: 1435 mm (Lines 5-9) | |
| Safety and Electrification | Electrification: The metro is powered by a 25 kV, 50 Hz AC OHE. |
| Signalling: The metro system will use Cab Signalling/Distance to Go (Lines 1-6), CBTC (Lines 7-9) | |
| Daily Ridership | 4.63 million+ passengers |

Delhi Metro’s Rolling Stock
As of March 2019, the Delhi Metro Rail Corporation (DMRC) maintained a fleet of 2,214 metro coaches, consisting of 1,352 broad gauge and 862 standard gauge units. To support the expansion plans under Phase 4, DMRC awarded Alstom with the contract to supply 312 coaches.
| Contract | Coaches | Manufacturer |
| RS1 | 240+40 | Mitsubishi – MELCO – BEML |
| RS2 | 340+84 | Bombardier Transportation |
| RS3 | 156+40 | Hyundai Rotem |
| RS4 | 64 | BEML |
| RS5 | 74+40 | Bombardier Transportation |
| RS6 | 136 | BEML |
| RS7 | 76 | Bombardier Transportation |
| RS9 | 162 | BEML – Hyundai Rotem |
| RS10 | 486+18 | Hyundai Rotem – BEML |
| RS11 | 162 | Bombardier Transportation |
| RS13 | 74+22 | BEML |
| RS14 | 24 | Cancelled (Airport Exp Line) |
| RS15 | 80 | BEML |
| RS16 | 40 | Bombardier Transportation |
| RS17 | 312 | Alstom Transport India |



Lines of Delhi Metro
| Operational: 351.28 km | Under Construction: 65.1 km | Approved: 20.76 km | Proposed: 35.76 km |
Phase 1: The construction of Phase 1 began in 1998 with the objective of establishing an approximately 65 km-long metro network in Delhi. The first operational segment extending 8.3 km from Shahdra to Tis Hazari was inaugurated on December 25, 2002. The entirety of Phase 1 was fully operational by 2006.
Estimated Cost: Rs 10,571 crore
Funding
Operational Lines
- Line 1 (Red Line): Shahdara – Rithala
- Distance: 22 km
- Stations (18): Rithala, Rohini West, Rohini East, Pitampura, Kohat Enclave, Netaji Subhash Place, Keshav Puram, Kanhaiya Nagar, Inderlok, Shastri Nagar, Pratap Nagar, Pul Bangash, Tis Hazari, Kashmere Gate, Shastri Park, Seelampur, Welcome, Shahdara

- Line 2 (Yellow Line): Vishwavidyalaya – Central Secretariat
- Distance: 11 km
- Stations (10): Vishwavidyalaya, Vidhan Sabha, Civil Lines, Kashmere Gate, Chandni Chowk, Chawri Bazaar, New Delhi, Rajiv Chowk, Patel Chowk, Central Secretariat
- Line 3 (Blue Line): Dwarka Sector 9 – Indraprastha
- Distance: 32.1 km
- Stations (30): Dwarka Sector 9, Dwarka Sector 10, Dwarka Sector 11, Dwarka Sector 12, Dwarka Sector 13, Dwarka Sector 14, Dwarka, Dwarka More, Nawada, Uttam Nagar West, Uttam Nagar East, Janakpuri West, Janakpuri East, Tilak Nagar, Subhash Nagar, Tagore Garden, Rajouri Garden, Ramesh Nagar, Moti Nagar, Kirti Nagar, Shadipur, Kirti Nagar, Patel Nagar, Rajendra Place, Karol Bagh, Jhandewalan, RK Ashram Marg, Rajiv Chowk, Barakhamba Road, Mandi House, Pragati Maidan, Indraprastha

Phase 1 Project’s Timeline
| Year | Details | |
| 2002 | Shahdara – Tis-Hazari (Red Line): 8.3 km | |
| 2003 | Tis Hazari – Inder Lok (Red Line): 4.1 km | |
| 2004 | March | Inder Lok – Rithala (Red Line): 8.9 km |
| December | Vishwa Vidyalaya – Kashmere Gate (Yellow Line): 4 km | |
| 2005 | July | Kashmere Gate – Central Secretariat (Yellow Line): 7 km |
| December | Dwarka – Barakhamba (Blue Line): 22.9 km | |
| 2006 | April | Dwarka – Dwarka Sector 9 (Blue Line): 6.5 km |
| November | Barakhamba – Indraprastha (Blue Line): 4.0 km | |
Phase 2: Following the success of Phase 1, the construction of Phase 2 started in 2006. This phase consisted of 124.93 km of route length and 86 stations. The first section opened in June 2008, and the last section was completed in August 2011.
Estimated Cost: Rs 18,783 crore
Funding Plan
- Line 4 (Blue Line): Yamuna Bank – Vaishali
- Distance: 8.74 km
- Stations (8): Yamuna Bank, Laxmi Nagar, Nirman Vihar, Preet Vihar, Karkarduma, Anand Vihar ISBT, Kaushambi, Vaishali
- Line 5 (Green Line): Inderlok – Mundka
- Distance: 15.15 km
- Stations (14): Inderlok, Ashok Park Main, Punjabi Bagh, Shivaji Park, Madipur, Paschim Vihar East, Paschim Vihar West, Peera Garhi, Udyog Nagar, Maharaja Surajmal Stadium, Nangloi, Nangloi Railway Station, Rajdhani Park, Mundka
- Line 5 (Green Line): Kirti Nagar – Ashok Park Main
- Distance: 3.31 km
- Stations (3): Kirti Nagar, Satguru Ram Singh Marg, Ashok Park Main
- Line 6 (Violet Line): Central Secretariat – Badarpur Border
- Distance: 20.16 km
- Stations (16): Central Secretariat, Khan Market, JLN Stadium, Jangpura, Lajpat Nagar, Moolchand, Kailash Colony, Nehru Place, Kalkaji Mandir, Govind Puri, Harkesh Nagar Okhla, Jasola Apollo, Sarita Vihar, Mohan Estate, Tughlakabad Station, Badarpur Border
- Airport Express Line (Orange Line): New Delhi – Delhi Aerocity
- Distance: 22.70 km
- Stations (4): New Delhi, Shivaji Stadium, Dhaula Kuan, Delhi Aerocity
Extensions of Existing Lines
- Line 1 (Red Line): Shahdara – Dilshad Garden
- Distance: 3.09 km
- Stations (4): Shahdara, Mansarovar Park, Jhilmil, Dilshad Garden
- Line 2 (Yellow Line): Vishwavidyalaya – Jahangipuri
- Distance: 6.36 km
- Stations (6): Vishwavidylaya, GTB Nagar, Model Town, Azadpur, Adarsh Nagar, Jahangirpuri
- Line 2 (Yellow Line): Central Secretariat – HUDA City Centre
- Distance: 27.58 km
- Stations (20): Central Secretariat, Udyog Bhawan, Lok Kalyan Marg (Race Course), Jorbagh, Dilli Haat INA, AIIMS, Green Park, Hauz Khas, Malviya Nagar, Saket, Qutab Minar, Chhatarpur, Sultanpur, Ghitorni, Arjan Garh, Guru Dronacharya, Sikanderpur, MG Road, IFFCO Chowk, Millennium (Guda) City Centre Gurugram
- Line 3 (Blue Line): Indraprastha – Noida City Centre
- Distance: 15.07 km
- Stations (12): Indraprastha, Yamuna Bank, Akshardham, Mayur Vihar 1, Mayur Vihar Extension, New Ashok Nagar, Noida Sector 15, Noida Sector 16, Noida Sector 18, Botanical Garden, Golf Course, Noida City Centre
- Line 3 (Blue Line): Dwarka Sector 9 – Sector 21
- Distance: 2.77 km
- Stations (3): Dwarka Sector 9, Dwarka Sector 8, Dwarka Sector 21
Phase 2 Project’s Timeline
| Year | Details | |
| 2008 | Shahdara – Dilshad Garden (Red Line): 3.1 km | |
| 2009 | February | Vishwa Vidyalaya – Jahangirpuri (Yellow Line): 6.4 km |
| May | Indraprastha – Yamuna Bank (Blue Line): 2.1 km | |
| November | Yamuna Bank – Noida City Centre (Blue Line): 13.1 km | |
| 2010 | January | Yamuna Bank – Anand Vihar (Blue Line): 6.3 km |
| April | Inderlok – Mundka (Green Line): 15.1 km | |
| June | Qutub Minar – Huda City Centre (Yellow Line): 14.5 km | |
| September | Central Secretariat – Qutub Minar (Yellow Line): 12.5 km | |
| October | Central Secretariat – Sarita Vihar (Violet Line): 15 kmDwarka Sector 9 – Dwarka Sector 21(Blue Line): 2.8 km | |
| 2011 | January | Sarita Vihar – Badarpur (Violet Line): 5.1 km |
| February | New Delhi Railway Station – Dwarka Sec 21 (Airport Express Line): 22.5 km | |
| July | Anand Vihar – Vaishali (Blue Line): 2.6 km | |
| August | Kirti Nagar – Ashok Park Main (Green Line): 3.3 km | |
Phase 3: The construction of Phase 3 began in 2011. It involved a total length of 162.495 kilometres, including 109 stations. The phase consisted of three new lines and extensions of existing lines from Phases 1 and 2. The last section of Phase 3 was completed in September 2021. Phase 3 was one of the most challenging construction phases due to its extensive underground sections totalling 54 km. DMRC deployed more than 20 TBMs simultaneously to facilitate the construction of underground sections.
Estimated Cost: Rs. 41,079 crore
Funding Plan
Introduction of 3 New Lines
- Line 7 (Pink Line): Majlis Park – Shiv Vihar
- Distance: 57.49 km
- Stations (18): Majlis Park, Azadpur, Shalimar Bagh, Netaji Subhash Place, Shakarpur, Punjabi Bagh West, ESI Basaidarpur, Rajouri Garden, Mayapuri, Naraina Vihar, Delhi Cantt, Durgabai Deshmukh South Campus, Sir Vishweshwaraiah Moti Bagh, Bhikaji Cama Place, Sarojini Nagar, Delhi Haat INA, South Extension, Lajpat Nagar, Vinobapuri, Ashram, Sarai kale Khan Hazrat Nizamuddin, Mayur Vihar 1, Mayur Vihar Pocket 1, Trilokpuri Sanjay Lake, East Vinod Nagar – Mayur Vihar II, Mandawali – West Vinod Nagar, IP Extension, Anand Vihar ISBT, Karkarduma, Karkarduma Court, Krishna Nagar, East Azad Nagar, Welcome, Jafrabad, Maujpur – Babarpur, Gokulpuri, Johri Enclave, Shiv Vihar
- Line 8 (Magenta Line): Janakpuri West – Botanical Garden
- Distance: 38.235 km
- Stations (25): Janakpuri West, Dabri Mor – Janakpuri South, Dashrath Puri, Palam, Sadar Bazar Cantonment, Terminal T1 IGI Airport, Shankar Vihar, Vasant Vihar, Munirka, RK Puram, IIT, Hauz Khas, Panchsheel Park, Chirag Delhi, Greater Kailash, Nehru Enclave, Kalkaji Mandir, Okhla NSIC, Sukhdev Vihar, Jamia Millia Islamia, Okhla Vihar, Jasola Vihar Shaheen Bagh, Kalindi Kunj, Okhla Bird Sanctuary, Botanical Garden
- Line 9 (Grey Line): Dwarka – Dhansa Bus Stand (Najafgarh)
- Distance: 5.340 km
- Stations (4): Dwarka, Nangli, Najafgarh, Dhansa Bus Stand
Extensions of Existing Lines
- Line 1 (Red Line): Dilshad Garden – Shaheed Sthal (New Bus Adda)
- Distance: 9.410 km
- Stations (9): Dilshad Garden, Shaheed Nagar, Raj Bagh, Major Mohit Sharma Rajendra Nagar, Shyam Park, Mohan Nagar, Arthala, Hindon River, Shaheed Sthal (New Bus Adda)
- Line 2 (Yellow Line): Jahangirpuri – Samaypur Badli
- Distance: 4.489 km
- Stations (4): Jahangirpuri, Haiderpuri Badli Mor, Rohini Sector 18-19, Samaypur Badli
- Line 3 (Blue Line): Noida City Centre – Noida Electronic City
- Distance: 6.82 km
- Stations (7): Noida City Centre, Noida Sector 34, Noida Sector 52, Noida Sector 61, Noida Sector 59, Noida Sector 62, Noida Electronic City
- Line 5 (Green Line): Mundka – Brigadier Hoshiyar Singh
- Distance: 11.182 km
- Stations (8): Mundka, Mundka Industrial Area (M.I.A), Ghevra Metro station, Tikri Kalan, Tikri Border, Pandit Shree Ram Sharma, Bahadurgarh City, Brigadier Hoshiar Singh
- Line 6 (Violet Line): Central Secretariat – Mandi House
- Distance: 3.23 km
- Stations (3): Central Secretariat, Janpath, Mandi House
- Line 6 (Violet Line): Mandi House – Kashmere Gate
- Distance: 6.04 km
- Stations (6): Mandi House, ITO, Delhi Gate, Jama Masjid, Lal Quila, Kashmere Gate
- Line 6 (Violet Line): Badarpur Border – Ballabgarh
- Distance: 16.91 km
- Stations (12): Badarpur Border, Sarai, NHPC Chowk, Mewala Maharajpur, Sector 28, Badkal Mor, Old Faridabad, Neelam Chowk Ajronda, Bata Chowk, Escorts Mujesar, Sant Surdas (Sihi), Raja Nahar Singh (Ballabhgarh)
- Airport Express Line (Orange Line): Dwarka Sector 21 – Yashbhoomi Dwarka Sector 25
- Distance: 2.01 km
- Stations (2): Dwarka Sector 21, Yashbhoomi Dwarka Sector 25
Phase 3 Project’s Timeline
| Year | Details | |
| 2014 | Central Secretariat – Mandi House (Violet Line): 3.03 km | |
| 2015 | June | Mandi House – ITO (Violet Line): 0.972 km |
| September | Badarpur – Escorts Mujesar (Violet Line): 13.875 km | |
| November | Jahangirpuri – Samaypur Badli (Yellow Line): 4.489 km | |
| 2017 | May | ITO – Kashmere Gate (Violet Line): 5.17 km |
| December | Botanical Garden – Kalkaji Mandir (Magenta Line): 12.64 km | |
| 2018 | March | Majlis Park-South Campus (Pink Line): 21.57 km |
| May | Janakpuri W – Kalkaji Mandir (Magenta Line): 25.26 km | |
| June | Mundka – Brigadier Hoshiyar Singh (Green Line): 11.182 km | |
| August | Durgabai Deshmukh South Campus – Lajpat Nagar (Pink Line): 8.1 km | |
| October | Trilokpuri Sanjay Lake – Shiv Vihar (Pink Line): 17.8 km | |
| November | Escorts Mujesar – Raja Nahar Singh (Violet Line): 3.205 km | |
| December | Lajpat Nagar – Mayur Vihar Pocket 1 (Pink Line): 9.7 km | |
| 2019 | March | Dilshad Garden – Shaheed Sthal/New Bus Adda (Red Line): 9.41 kmNoida City Centre – Electronic City (Blue Line): 6.675 km |
| October | Dwarka – Najafgarh (Grey Line): 4.295 km | |
| 2021 | August | Mayur Vihar Pocket 1 and Trilokpuri – Sanjay Lake (Pink Line): 1.38 km |
| September | Najafgarh – Dhansa Bus Stand (Grey Line): 1.218 km | |
Phase 4: Construction of Delhi Metro’s Phase 4, initiated in 2019, is set to expand the network by an additional 103 kilometres. Once completed, the total length of the Delhi Metro will surpass 450 kilometres. Presently, construction efforts are concentrated on three priority corridors, covering a combined distance of 65.1 kilometres.
| Expected to be operational by 2026.Estimated Project Cost: Rs. 24,948.65 croreAll the lines in Phase 4 will use fully driverless technology. |
Funding Pattern for Delhi Metro’s Phase 4
Under -Construction Lines in Phase 4
- Line 10 (Golden Line): Tughlakabad – Terminal 1 IGI Airport
- Distance: 23.622 km
- Type: Elevated (4.279 km) and Underground (19.343 km)
- Stations (15): Tughlakabad, Tughlakabad Railway Colony, Anandmayee Marg, Sangam Vihar – Tigri, Khanpur, Ambedkar Nagar, Saket G-Block, Neb Sarai, IGNOU, Chhatarpur Mandir, Chhatarpur, Kishangarh, Vasant Kunj Sector-D, Mahipalpur, Delhi Aerocity, Terminal 1-IGI Airport
| In August, the YFC Project launched its first U-girder for the 23.62 km Delhi Metro’s Golden Line, connecting Aerocity to Tughlakabad via 15 stations. |
- Line 7 (Pink Line’s Extension): Majlis Park – Maujpur – Babarpur
- Distance: 12.32 km
- Stations (8): Majlis Park, Burari Crossing, Jharoda Majra, Jagatpur Village, Soorghat, Sonia Vihar, Khajuri Khas, Bhajanpura, Yamuna Vihar, Maujpur-Babarpur
- Line 8 (Magenta Line’s Extension): Janakpuri West – R.K. Ashram
- Distance: 29.6 km
- Stations (22): Krishna Park Extn, Keshopur, Paschim Vihar, Peeragarhi, Mangol Puri, West Enclave, Pushpanjali, Deepali Chowk, Pitampura, Prashant Vihar, North Pitampura, Haiderpur Badli Mor, Bhalaswa, Majlis Park, Azadpur, Ashok Vihar, Derawal Nagar, Ghanta Ghar, Pulbangash, Sadar Bazar, Nabi Karim, Ramakrishna Ashram Marg
Major Contractors of Delhi Metro Phase 4
| Contract | Contractor |
| DCS-1B Phase 4 Consultant | PADECO – Mott MacDonald – Hill – BARSYL consortium |
| Centralised Management System for Construction Workers of Phase 4 | Planet E-Com Solutions Pvt. Ltd. |
| RS-17: 312 Coach Rolling Stock Contract | Alstom Transport India |
| DT-02R: Manufacturing & Supply of 16935 MT Head Hardened Rails | Jindal Steel & Power Ltd. (JSPL) |
| DS-16: Closed Circuit Television (CCTV) System for 3 Priority Corridors of Phase 4 | Tata Advanced Systems (TAS) Ltd. |
| DS-24: Automatic Fare Collection (AFC) System for 44 stations of Phase 4 | France SAS – Paytm Payments Bank JV |
| DS-14: Radio System for 3 priority corridors of Phase 4 | Motorola Solutions India |
Phase 4 Project’s Timeline
| Year | Details | |
| 2018 | December | Phase 4 of the Delhi Metro, including six lines, got approval from the government of Delhi. |
| 2019 | March | The central government approved three priority corridors of the Delhi Metro. |
| December | Construction of the 65.1 km corridor began. | |
Approved Lines in Phase 4
- Line 11 (Brown Line): Lajpat Nagar – Saket G-Block
- Distance: 8.4 km
- Stations (8): Saket-G Block, Pushp Vihar, Saket District Court, Pushpa Bhawan, Chirag Dilli, Greater Kailash-1, Andrews Ganj, Lajpat Nagar
- Line 5 (Green Line Extension): Inderlok – Indraprastha
- Distance: 12.38 km
- Stations (10): Inderlok, Dayabasti, Sarai Rohilla, Ajmal Khan Park, Nabi Karim, New Delhi Railway Station, LNJP Hospital, Delhi Gate, IG Stadium, Indraprastha
Proposed Lines in Phase 4
- Line 1 (Red Line Extension): Rithala – Nathupur (Kundli)
- Distance: 27.32 km
- Station (21): Rohini Sector 25, Rohini Sector 26, Rohini Sector 31, Rohini Sector 32, Rohini Sector 36, Barwala, Rohini Sector 35, Rohini Sector 34, Bawana Industrial Area – 3 & 4, Bawana Industrial Area –1 & 2, Bawana JJ Colony, Sanoth, New Sanoth Colony, Depot Station, Bhorgarh Village, Anaj Mandi Narela, and Narela DDA Sports Complex, Narela, Narela Sector 5, Kundli and Nathupur
| On September 4, 2024, transport minister Kailash Gahlot announced that the Rithala – Narela corridor will extend to Kundli – Nathpur in Haryana. The Delhi government has approved the extension and the proposal will now be sent to the central government to plan and announce the tenders for the project. |
- Line 3 (Blue Line Extension): Noida Electronic City – Sahibabad
- Distance: 5.2 km
- Stations (5): Vaibhav Khand, Indirapuram, Shakti Khand, Vasundhra Sector 5, Sahibabad (interchange)
- Delhi Metrolite: Kirti Nagar – Bamnoli Village
- Distance: 19.09 km
- Stations (21): Kirti Nagar, Saraswati Garden, Mayapuri Bus Depot, Mayapuri, Hari Nagar Block BE, Mayapuri Industrial Area, Mayapuri Industrial Area-II, Tihar Jail, Shivpuri, Dabri Village, Sitapuri Extension, Mahavir Enclave, Dwarka Sector 2, Dwarka Sector 7, Dwarka Sector 6, Dwarka Court, Dwarka Sector 20, Dwarka Sector 23, Dhul Siras Village, ECC Dwarka, Bamnoli Village
Recent Updates on Phase 5
According to former DMRC managing director E. Sreedharan, Delhi will require Phase 5 after completing Phase 4. This suggestion highlights the need to handle the rising demand for public transportation by the growing population. The corridor proposal is not yet done, but there are a few recommendations.
- Yamuna Bank – Loni (12 km): Eliminated from Phase IV expansion
- The Central Vista Redevelopment Project includes the Central Vista Loop Line.
- The Indira Gandhi International Airport development includes the Delhi Air Train, also known as the Automated People’s Mover, providing links with Aerocity, T1, T2, and T3.
- The DPR has been prepared for the Delhi Metro Yellow Line’s expansion from Samaypur Badli metro station to Khera Kalan in North Delhi, with a stop in Siraspur.
DMRC’s Initiatives to Streamline Passenger Comfort
| Airport Check-In ServicesSince the first week of June, DMRC has introduced check-in facilities for international flights at New Delhi and Shivaji Stadium metro stations on the Airport Express Line. Passengers can check in their luggage at these two metro stations, and the authorities will transport it to the airport using advanced automated systems. Multiple TicketsThe passengers can purchase up to 6 Single Journey QR Tickets with the same origin and destination for a group of family or friends. Multiple QR Tickets will be issued, allowing multiple entries and exits for each ticket. |
Challenges Faced by the Delhi Metro
- Overcrowding
The high ridership in metros has led to overcrowding, leading to delays in the metro arrivals. Steps have been taken to address the issue, and eight coach trains have been introduced along the yellow and blue lines.
- Rising Fares
The fares for the Delhi metro are higher than those for the bus services. They are the second-most unaffordable metro, charging less than US$0.5 per ride.
Benefits of Metro in Delhi
- Addressing the Environmental Concerns
Following the New York City Subway, the Delhi metro is ranked second worldwide in holding an ISO 14001 certification for environmentally friendly construction. The metro has won awards for its environmentally friendly practices from the United Nations, RINA, and the International Organization for Standardization. Rainwater collection and rooftop solar power plants are features of the network that help safeguard the environment.
- Interchange Stations
Delhi Metro plans to expand its number of triple interchange stations from three to four. At present, there is only one triple exchange station, Kashmiri Gate, and the Azadpur metro station is under construction. The New Delhi metro station and Lajpat Nagar will soon become triple exchange stations.
Conclusion
The Delhi Metro has transformed urban transportation, reducing traffic congestion and pollution while enhancing city connectivity. Its extensive network highlights a commitment to sustainable and efficient transit solutions. The ongoing expansions show the system’s adaptability to growing demands and its role in shaping a modern, eco-friendly metro system. Despite challenges like overcrowding and rising fares, the Delhi Metro offers significant environmental benefits, showcasing its crucial role in Delhi’s infrastructure and urban planning.








