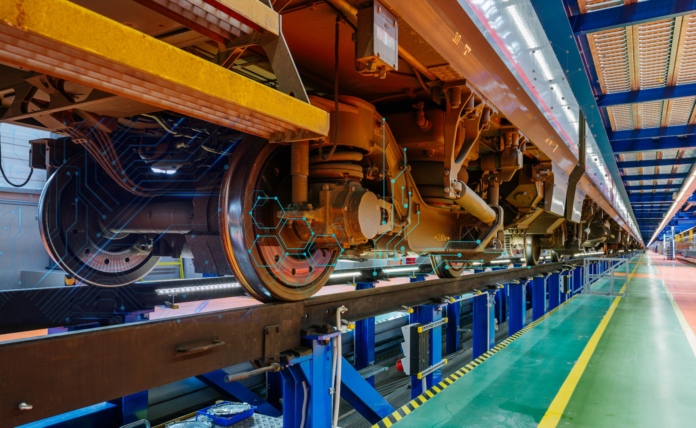
Introduction
Railway systems across the world are moving towards a new era of mobility. In this new era they are becoming data-driven to improve reliability, safety, and efficiency in rail operations. The expansion of rail networks, development of modern and faster rolling stock, and the growing demand for punctual services, managing vast and complex railway assets are together acting as a critical challenge for rail operators. In this context, predictive analytics is gaining attention as a resolution tool for these challenges that enables railway organistaions to transition from reactive maintenance and decision-making processes to proactive and data-informed management of railway assets.
Predictive analytics involves the use of statistical algorithms, machine learning models, and data mining techniques to analyse historical and real-time data for identifying patterns and predicting future outcomes of railway assets. In railways, this approach helps anticipate component failures, optimise maintenance schedules, forecast demand, and improve asset utilisation. Data from multiple sources such as sensors installed on tracks, locomotives, and signaling systems, along with weather and operational data, are collected and processed to generate actionable insights.
The global railway sector has increasingly adopted predictive maintenance and analytics solutions to improve asset reliability and prevent unplanned downtime. There are many countries in the world including Germanym, Japan, and the United Kingdom that have implemented predictive systems for the monitoring of various railway assets such as tracks, wheels and other minor and major rail components.
In India, the Indian Railways has begun deploying AI-based predictive tools and condition monitoring systems under its broader digital transformation initiatives. A prime example is the Madhepura Electric Locomotive Factory, a joint venture between Alstom (74%) and Indian Railways (26%), which is responsible for manufacturing 800 Prima T8 WAG-12B locomotives for freight operations. To ensure the optimal performance of these high-power locomotives, two ultramodern maintenance depots have been established at Saharanpur and Nagpur, both designed to utilise predictive maintenance technologies for real-time diagnostics and reliability improvement.
As railway networks continue to modernise, predictive analytics represents a fundamental shift in how decisions are made moving towards a model where maintenance, scheduling, and operations are guided by data-driven predictions rather than routine inspections or reactive responses which are cost intensive and time taking.
This article explores the concept of predictive analytics in railways, its applications in maintenance and operations, the underlying data infrastructure, global and Indian case studies, and how these technologies are driving operational excellence across the railway ecosystem.
Understanding Predictive Analytics in Railways

Predictive analytics in the railway sector is a data-driven approach that uses statistical models, artificial intelligence (AI), and machine learning (ML) algorithms to predict potential system failures, optimise maintenance schedules, and improve overall network efficiency. It forms a part of the broader domain of data analytics and asset intelligence, which further helps rail operators to make informed decisions based on data patterns rather than routine inspection cycles or human judgment alone.
In a railway environment, data is continuously generated from multiple assets and operational systems. This includes information from track circuits, axle counters, onboard sensors, signaling equipment, traction motors, brake systems, and even weather monitoring instruments. These data points are collected through Internet of Things (IoT) devices and transmitted to centralised platforms for processing and analysis.
By integrating ML models, the system identifies abnormal patterns or early indicators of deterioration in assets such as wheels, bearings, traction motors, and overhead equipment.
A key element of predictive analytics is its ability to integrate data from diverse subsystems rolling stock, track infrastructure, signaling, and power supply into a unified analytical framework. This integration enables cross-functional insights, such as correlating vibration data from wheelsets with track geometry variations or linking power consumption anomalies with traction motor performance. Such correlations provide actionable intelligence that supports timely maintenance interventions, thereby minimizing the likelihood of unexpected failures and service disruptions.
Globally, rail operators are adopting predictive analytics platforms that combine real-time monitoring with digital twins virtual replicas of physical assets that simulate behavior under different operational conditions. These digital twins help in testing scenarios, predicting wear rates, and planning asset replacements more accurately. In India, similar approaches are being introduced within locomotive and track monitoring systems, helping engineers move from schedule-based maintenance to condition-based strategies.
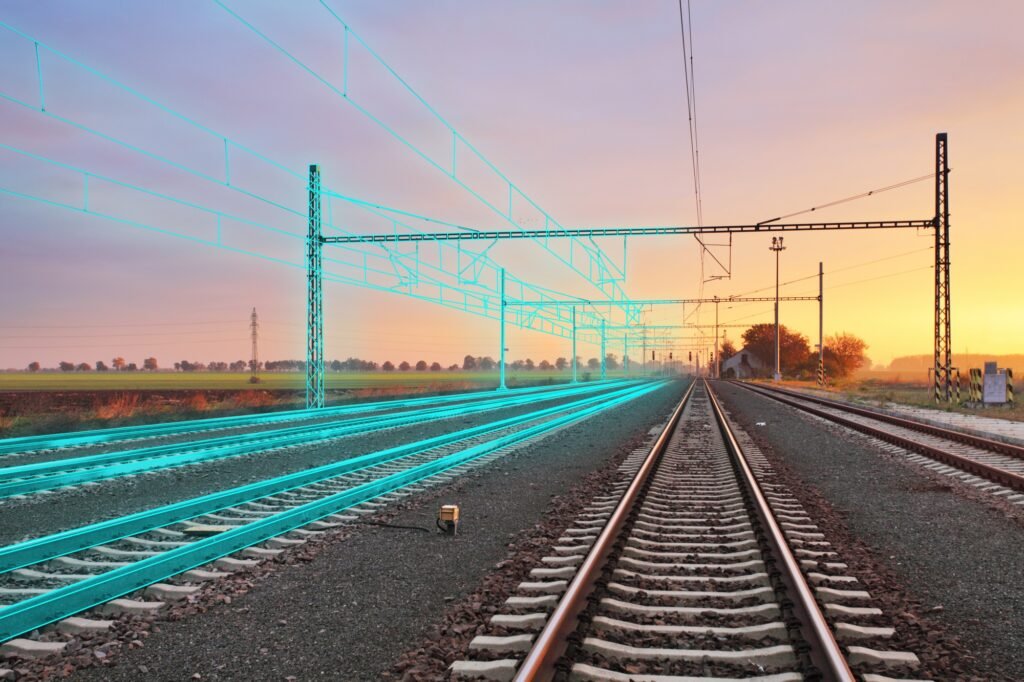

For example: Deutsche Bahn (DB), which manages a network of approximately 33,000 kilometres of track and 5,700 stations throughout Germany, is among the leaders in this transformation. Its subsidiary, DB Digital Services (DSD), aims to improve network efficiency without expanding physical infrastructure. In partnership with NVIDIA, DSD is developing the first country-scale digital twin capable of simulating automatic train operations across the entire German network. This model provides a photorealistic and physically accurate virtual environment, allowing DB to optimise scheduling, test new systems, and predict infrastructure behaviour under real-world conditions before implementation.
Applications of Predictive Analytics in Railway Operations

Predictive analytics has become an essential component of modern railway operationsad as it is capable of addressing a wide range of use cases from asset maintenance to passenger management. WIth the help of large volumes of operational data, railway and metro operators can anticipate system behavior which can further be utilised for minimising unplanned disruptions, and optimise resource allocation. The following are key domains where predictive analytics can make improvements in efficiency and reliability.
Predictive Maintenance
One of the direct applications of predictive analytics in railways & metros is predictive maintenance, which allows operators to monitor the condition of assets in real time and identify potential failures before they occur. Traditional maintenance methods rely on fixed schedules or manual inspections, which often lead to either premature part replacement or delayed interventions. Predictive maintenance, on the other hand, uses real-time data collected from sensors attached to locomotives, bogies, wheels, and tracks to estimate the remaining useful life (RUL) of each component.
Machine learning models analyse parameters such as temperature, vibration, acoustic emissions, and electrical current to detect early signs of wear or malfunction. For instance, abnormal vibration patterns can indicate developing wheel flats, while temperature spikes may suggest bearing or brake system issues. In India, the adoption of AI-driven condition monitoring for high-capacity freight locomotives, such as the WAG-12B series produced by Alstom, demonstrates how predictive insights can enhance locomotive availability and reduce unscheduled downtime.

Globally, predictive maintenance systems implemented by operators such as Deutsche Bahn (Germany) and Network Rail (UK) have led to measurable improvements in asset reliability, optimising maintenance costs and extending component life cycles.
Network Efficiency and Scheduling
Railway networks are complex systems where operational performance depends on the synchronisation of multiple variables train movements, track capacity, crew availability, and passenger demand. Predictive analytics supports timetable optimisation and network management by processing historical traffic data and real-time operational inputs to forecast congestion, delays, and capacity bottlenecks.
This approach allows control centers to allocate slots more efficiently, optimise headways, and minimise disruptions during peak hours. In freight operations, predictive analytics enhances asset rotation by estimating wagon turnaround times and optimising train formation based on route demand which can contribute directly to higher throughput.
Safety Management
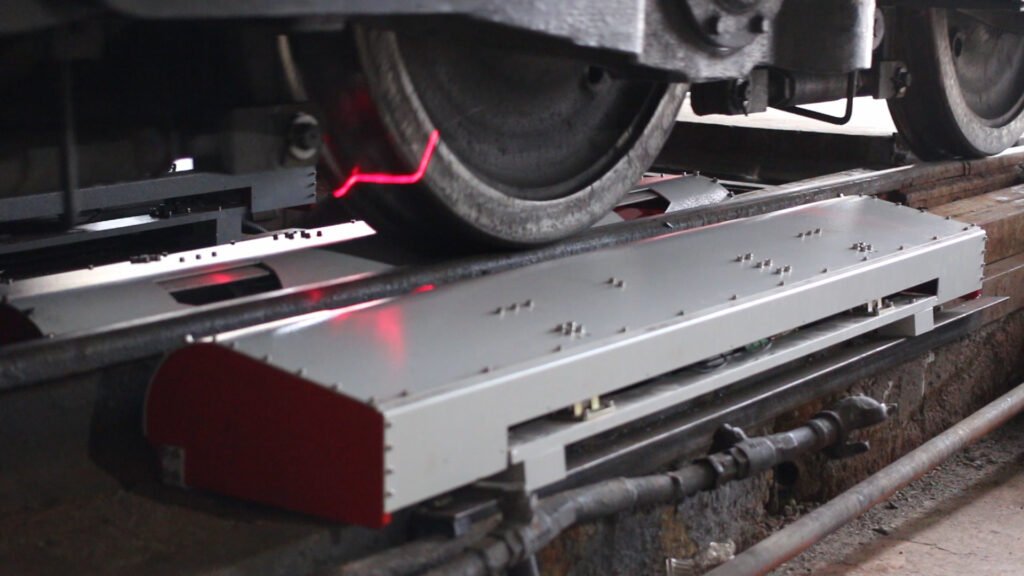

Safety is the foundation of railway operations, and predictive analytics contributes to accident prevention by identifying risks before they lead to incidents. Data from track geometry measurement systems, wayside detection units, and overhead equipment sensors are analysed to predict structural weaknesses, potential derailments, or signal failures.
AI models detect anomalies such as rail surface cracks, misalignments, or excessive track wear, which empowers maintenance teams to act before conditions deteriorate to unsafe levels. Some advanced systems integrate predictive analytics with Automatic Train Protection (ATP) and Kavach-like technologies to further increase operational safety and reduce human dependency in fault detection.
Passenger Experience, Demand Forecasting, and Crowd Management
Predictive analytics also plays a crucial role in improving the passenger experience by enabling operators to anticipate demand, adjust capacity, and manage service quality. Using data from ticketing systems, sensors, and mobile applications, predictive models estimate passenger flow trends for specific routes, seasons, or events. This information allows operators to optimise rolling stock allocation, and resource deployment.
A growing area of application is crowd management and passenger safety. Data acquired from sensors, surveillance systems, and automated passenger counters integrated at stations can be analysed to assess crowd density in real time. These insights help railway authorities manage passenger volume, prevent overcrowding, and respond quickly to potential safety risks. In the context of Indian Railways, and metro systems, crowd management at stations and platforms is a persistent challenge, especially during festive seasons when passenger volumes surge beyond normal capacity.
In the past, overcrowding has resulted in serious accidents and casualties. A tragic example occurred on February 15, 2025, when a stampede at New Delhi Railway Station led to the death of at least 18 people and left 15 others injured. Such incidents highlight the urgent need for continuous crowd monitoring and early-warning systems. Predictive analytics, combined with video analytics and AI-based alert mechanisms, can play a vital role in forecasting crowd buildup which enable timely interventions such as regulating entry points, deploying additional staff, or adjusting train schedules to disperse congestion.
In urban metro systems, passenger density forecasts help manage crowd flow and improve station-level service management. For Indian Railways, integrating predictive demand forecasting and crowd analytics with the National Rail Plan can support long-term planning for safer and more efficient passenger operations.
Data Infrastructure and Technology Framework

The effectiveness of predictive analytics in railways depends heavily on the quality, availability, and integration of data collected from diverse operational assets. A strong data infrastructure forms the foundation of this ecosystem, and facilitates the acquisition, transmission, storage, and analysis of large volumes of information generated by rolling stock, track systems, signaling equipment, and passenger interfaces.
Internet of Things (IoT)
Internet of Things (IoT) network remains at the core of predictive analytics it connects the multiple sensors and devices embedded on the rolling stock, track. These sensors continuously record parameters such as vibration, temperature, current, pressure, and acceleration from locomotives, bogies, and tracks. The data is transmitted through edge computing or onboard communication modules to centralised control centers or cloud-based data platforms.
Big Data, ML & AI
Once acquired, the data is stored in Big Data architectures such as data lakes or distributed storage systems that can handle structured and unstructured data from multiple sources. Advanced analytics platforms, often supported by cloud service providers like AWS, Microsoft Azure, or Google Cloud, are used to run machine learning (ML) and artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms on this data. These platforms enable scalability and real-time analytics, and support both immediate operational decisions and long-term trend analysis.
Cybersecurity Framework

A secure and resilient data infrastructure is equally critical for the safe and efficient rail operation. As the reliance of railway systems increases on digital systems, cybersecurity frameworks must be embedded within the predictive analytics architecture.
The IEC 62443 series is widely used across industries and provides a clear framework for protecting industrial automation and control systems, including those in railway networks, devices, and operations centers. However, IEC 62443 has limitations when applied to large, distributed, and interconnected railway environments, where multiple systems operate together.
To address these challenges, the CENELEC Technical Specification TS 50701 was developed specifically for the railway sector. It provides guidance on how to apply cybersecurity principles to railway operations, covering rolling stock, signaling, communication, and control systems. TS 50701 bridges the gaps left by IEC 62443 and aligns cybersecurity requirements with the operational characteristics of railways.
Predictive Analytics Applications in Global Rail Operations
Deutsche Bahn, Germany

Deutsche Bahn (DB), Germany’s national railway operator, has implemented predictive analytics to improve infrastructure maintenance and network performance. With an investment of €66 million, DB has developed advanced data-driven systems to detect faults early and plan maintenance more efficiently. According to a 2019 DB report, the use of predictive maintenance helped prevent approximately 3,600 infrastructure defects.
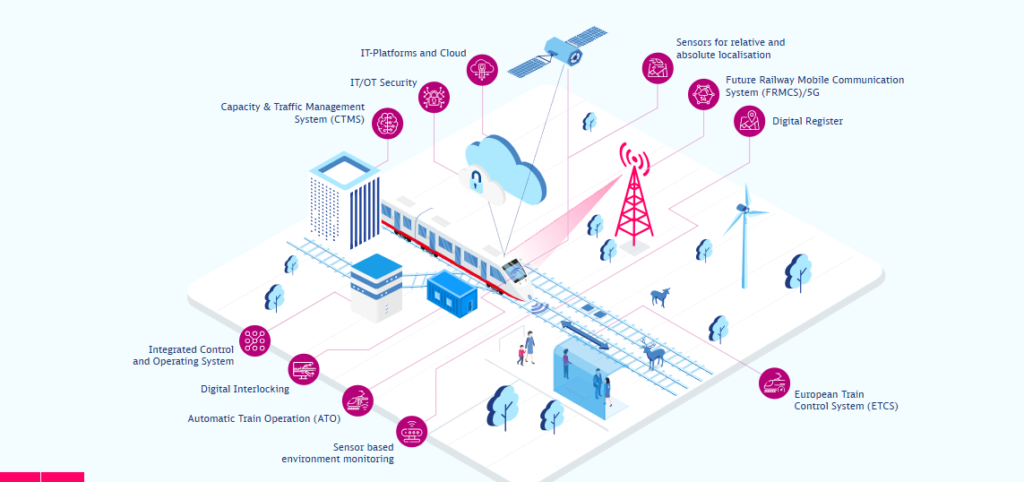
A key element of this initiative is the DIANA platform (Diagnosis and Analysis), developed jointly by DB Engineering & Consulting and Infraview. DIANA integrates data from multiple digital sources, including sensors, control systems, and maintenance records, to create a comprehensive overview of asset conditions across the rail network. This centralised system allows engineers to monitor real-time performance, identify patterns of degradation, and predict potential failures before they affect train operations.
By analysing large datasets using machine learning and statistical models, DIANA supports condition-based maintenance and optimises maintenance schedules.
Network Rail, United Kingdom
The United Kingdom’s Network Rail has implemented predictive analytics for track and infrastructure maintenance through its Intelligent Infrastructure (II) Programme, a digital transformation initiative under Control Period 6 (2019–2024). The programme aimed to transition railway asset management from a reactive to a predictive maintenance model, using data from over 20,000 miles of rail network. It integrates cloud computing (via Microsoft Azure), Ellipse (Network Rail’s asset management system), and advanced analytical tools to convert raw data into actionable insights.
Through the II framework, maintenance teams can monitor assets in real time, assess their condition, and predict potential failures well in advance. The flagship tool, Insight, combines data from measurement trains, aerial surveys, and remote sensors to present a unified view of the railway network. This helps plan interventions proactively, improving safety, reliability, and operational efficiency.
The initiative also involves developing digital record systems, mobile applications, and a national relay database to enhance data accuracy and accessibility.
Japan Railways (JR Group), Japan
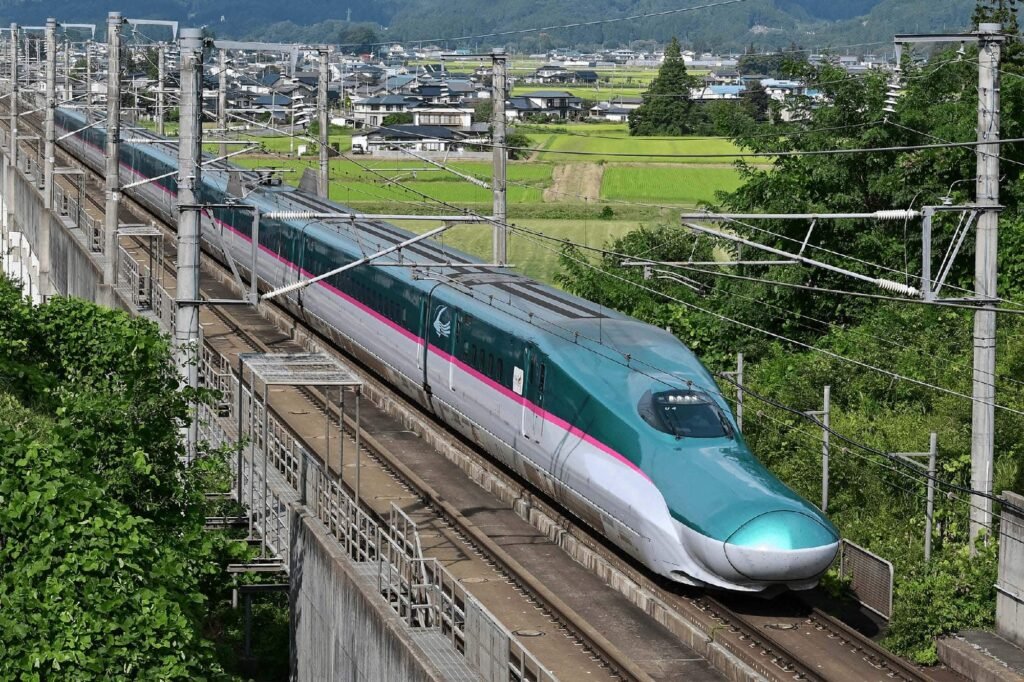

Japan Railways (JR Group) has integrated predictive analytics, which uses Artificial Intelligence and the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), into its maintenance and operations systems to support one of the world’s most punctual and safe rail networks.
JR uses “Doctor Yellow” high-speed inspection trains, equipped with advanced cameras and sensors, to measure track geometry, rail alignment, and overhead lines. JR Central has equipped its Tokaido-Shinkansen trains with AI systems that use in-line cameras, laser scanners, and near-infrared lighting to inspect overhead wires and poles while in operation.
The Roadblocks in Implementing Predictive Analytics in Indian Railways

Predictive analytics offers multiple benefits when applied at scale in railway operations. It has the potential to support the management of large and complex networks such as Indian Railways, where the movement of millions of passengers and vast freight volumes must be managed efficiently. The approach not only delivers substantial cost savings through optimised maintenance and reduced equipment failures but also minimises train disruptions and service delays. However, its large-scale implementation brings several operational, technical, and organisational challenges. These challenges become more complex in a system like Indian Railways, where legacy assets, extensive infrastructure, and regional variations create additional layers of difficulty.
1. Data Quality and Integration
Predictive analytics depends heavily on the accuracy and consistency of data. In railway systems, data originates from different sources such as rolling stock sensors, track monitoring units, signaling systems, and maintenance logs. These systems often operate independently and use different data formats, which makes their integration difficult.
2. High Implementation Costs
Developing and maintaining a predictive analytics ecosystem involves high initial costs. The installation of sensors, establishment of data centers, cloud computing services, and skilled manpower require capital expenditure. While the long-term benefits often outweigh these costs, budget constraints can delay adoption.
3. Legacy Infrastructure and System Compatibility
A major challenge in applying predictive analytics to indian railways is the coexistence of modern digital assets with decades-old mechanical and electrical systems. Many assets, such as locomotives and signaling equipment, were not designed for continuous data transmission.These assets require Retrofitting with IoT sensors and communication modules which can be technically complex and expensive.
4. Skill Gaps
Predictive analytics also requires a workforce that is skilled in handling the intricacies of these system. However, in Indian Railways the workforce is trained to manage the traditional systems. For the efficient implementation of Predictive analytics, it is imperative to upskilling maintenance and operations teams to interpret analytical outputs and take informed decisions is a gradual process. The development of in-house analytical capacity and promoting data literacy will play major role in overcoming these barriers.
Conclusion
Railway systems across the world are heading to a technological transformation where the data driven systems will empower them to utilise the full capacity of infrastructure. Predictive analytics is gradually changing the way railways operate and maintain their assets. It uses real-time data, historical patterns, and advanced algorithms which empowers the rail operators to anticipate equipment failures, optimis maintenance schedules, and enhance overall system reliability. India’s railway system which is currently the 4th largest railway in the world, can see it as practical solution to improve asset utilisation, reduce operational costs, and increase passenger safety without adding infrastructure overhead.
However, its success will completely depend on resolution of the challenges mentioned in earlier in this article. Railway authorities and government need to create an ecosystem where this technology can evolve and help Indian railways to become one of the efficient, safe railways in the world.
In essence, predictive analytics is not merely a technological upgrade it is a strategic shift towards, a more responsive, data-centric, and resilient railway system that can meet the growing demands of modern mobility in India.
Explore how AI-integrated systems are improving comfort, connectivity, and accessibility for passengers across metro and rail networks at the 6th edition of InnoMetro, India’s leading expo for the Metro & Railway industry which is going to held on 21-22 May 2026 at Bharat Mandapam, New Delhi
Register now: https://innometro.com/visitor-registration/








