Introduction
Indore is the largest and most populous city in Madhya Pradesh, India, serving as the state’s commercial, educational, and financial hub. It has been recognised as India’s cleanest city for seven consecutive years. Located on the Malwa plateau at an altitude of 553 meters above sea level, Indore is positioned along the banks of the Saraswati and Khan rivers. Indore is also the largest metropolitan area in Central India.The city functions as a central business zone, with more than 1,000 factories and a major industrial area (Pithampur), which is known for its automotive and pharmaceutical manufacturing sectors.
Growing Population and the Need for a Metro System in Indore
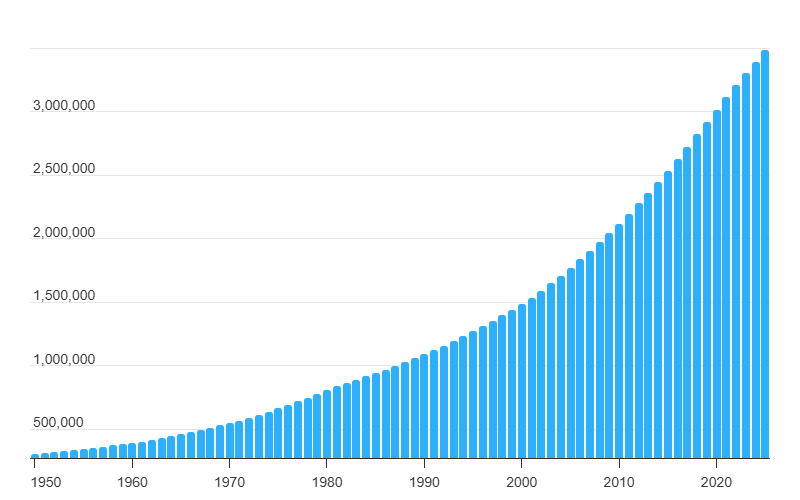
Indore’s Total Population By Year
The metro area population of Indore has shown a remarkable and consistent rise since 1950, as reflected in the graph. From a modest figure of under 200,000 residents in 1950, the population has surged past 3 million by 2025. This rapid growth, especially over the past two decades, has placed immense pressure on the city’s infrastructure, road networks, and public transport systems.
The surge in population has led to an increase in the number of private vehicles in the city, resulting in severe traffic congestion, longer commute times, and escalating air pollution. These challenges underscore the pressing need for a modern, high-capacity transit system for the city.

Indore Metro: A New Era of Urban Mobility
Overview
The Indore Metro is an under-construction Mass Rapid Transit System (MRTS) designed to serve Indore. The project is being developed by the Madhya Pradesh Metro Rail Co. Limited (MPMRCL).
Phase 1 of the Indore Metro consists of one metro corridor (Yellow Line), which spans 33.53 km, connecting Palasia – Railway Station – Rajwara – Airport – Bhawarsala – MR10 – Palasia (Ring Line).
On May 31, Prime Minister Narendra Modi inaugurated the Super Priority Corridor of Indore Metro, which is a part of Indore Metro’s Yellow Line. The super priority corridor spans 6 km, featuring 5 stations.
- Stations: Gandhi Nagar, Super Corridor 6, Super Corridor 5, Super Corridor 4, Super Corridor 3
Planning and Approval
- The master plan for the Indore Metro was prepared by Rohit Associates, Cities & Rails Pvt. Ltd. It envisions a 94 km network consisting of four metro lines and two spurs crisscrossing the city. For Phase 1, the Yellow Line (Line-3), designed as a ring line, was chosen for implementation.
- The Detailed Project Report (DPR) for Phase 1, spanning 33.53 km, was approved by the state government in December 2016 and by the Central Government’s cabinet in October 2018.
- The Chief Minister of Madhya Pradesh laid the foundation stone for the project in September 2019. Construction work began in February 2019, and the project is expected to be completed by 2027.

Key Specification
| Speed and Track | Top Speed: 80 kmph |
| Average Speed: 34 kmph | |
| Standard Gauge: 1435 mm | |
| Electrification | 750 V DC Third Rail |
| Signalling | Communication-based Train Control (CBTC) |
| Estimated Daily Ridership | 2.50 lakh/day (2027) |
| Estimated Cost | Rs.7500.80 crore |

Funding Mechanism of Indore Metro
The Indore Metro Rail Project will be financed partly from the Central Government and the State Government of Madhya Pradesh on an equal equity basis and partly as a loan from the Asian Development Bank (ADB) and the New Development Bank (NDB).
The total cost of the Project is estimated to be USD 1,200 million.
The NDB will finance USD 225 million, accounting for 18.8% of the total estimated cost. The Project is proposed to be co-financed with the Asian Development Bank under a parallel co-financing arrangement.
| Source of Fund | Amount |
| New Development Bank | 225 USD Million |
| Other Banks | 250 USD Million |
| Counterpart Funds | 725 USD Million |
Rolling Stock for Indore Metro
- In May 2022, Alstom secured the contract for the rolling stock of the Indore Metro from the Madhya Pradesh Metro Rail Corporation Limited (MPMRCL). The contract entails the supply and manufacturing of 25 trainsets, consisting of 75 coaches, for the Indore Metro Rail Project.
- In March 2023, Alstom commenced the manufacturing of these trainsets at its facility in Savli, Gujarat. Subsequently, in August 2023, Alstom delivered a three-coach trainset for the Indore Metro.
- In July 2025, Alstom delivered the 15th trainset for the Indore Metro Rail Project.

Contactor’s List
| Contract | Contractor |
| Detailed Project Report (DPR) Preparer | Rohit Associates Cities & Rails Pvt.Ltd |
| General Consultant (GC) | DB Engineering & Consulting GmbH – Geodata Engineering S.p.A. – Louis Berger Group JV |
| IN-02A/01: Construction of 5.29 km viaduct between ISBT/MR10 Flyover – Mumtaj Bag Colony | Dilip Buildcon Ltd. |
| IN-04: Construction of 5.2 km viaduct and 5 elevated stations between Shaheed Bagh – Palasia Chauraha | RVNL – URCC JV |
| IN-05R: Construction of twin tunnels (up & down by shield TBM), cut & cover, cross-passages with/without sump, ramps, and 7 underground stations | HCC – TPL Indore Metro JV |
| IN-08: Ballastless Track of Standard Gauge for the underground corridor and the Gandhi Nagar Depot | Texmaco Rail – ISC Projects JV |
| IN-09: Electrification – 750 V DC 3rd Rail, SCADA, Power Supply, RSS, TSS & ASS | Kalpataru Power Transmission (KPTL) |
| BH-IN-02: 156 Rolling Stock Cars for Bhopal & Indore metros, including Signaling and Train Control and Telecommunication Systems | Alstom Transport |
Indore Metro Route Details
| Operational | 6 km |
| Under Construction | 25.3 km |
| Approved | 57.18 km |
Phase 1
Yellow Line (Line-3): Palasia – Railway Station – Rajwara- Airport – Bhawarsala – MR10 – Palasia (Ring Line)
- Length: 33.53 km
- Type: Elevated & Underground
- Status: 16.217 km is under construction between Gandhi Nagar – Mumtaj Bag Colony
- Depot: Super Corridor
- Number of Stations: 29
- Station Names: Bhawarsala Square, MR 10 Road, ISBT / MR 10 Flyover, Chandragupta Square, Hira Nagar, Bapat Square, Meghdoot Garden, Vijay Nagar Square, Radisson Square, Mumtaj Bag Colony, Bengali Square, Patrakar Colony, Palasia Square, Indore Railway Station, Rajwada Palace, Chota Ganpati, Bada Ganpati, Ramchandra Nagar Square, BSF / Kalani Nagar, Airport, Gandhi Nagar Nanod, Super Corridor 6, Super Corridor 5, Super Corridor 4, Super Corridor 3, Super Corridor 2
| Recent Development on the Yellow Line Rail Vikas Nigam Ltd. and URC Construction (RVNL–URCC) Joint Venture has commenced the casting of box segments for Package IN-04. These segments will be utilized in constructing the viaduct that will link the elevated stations included in this package. In March 2024, RVNL–URCC secured Package IN-04 of the Indore Metro project from the MPMRCL at a value of Rs. 543 crore. Stations: Shaheed Bagh, Khajrana Chauraha, Bengali Chauraha, Patrakar Colony, Palasia Chauraha |

Indore Metro Proposed Lines
Line-1A: Sri Aurobindo Hospital – Collectorate office – Indore Bypass 1
- Number of Stations: 18
- Station Names: Sri Aurobindo Hospital, Bhawarsala Square, Sanwer Industrial Area, Ganesh Sham Colony, Banganga, Laxmibai Nagar Square, Mara Mata Square, Imli Bazar Chowk, Rajwada Palace, Collectorate Office, Indore Icchapur Rail Crossing, Tower Square, Bhawarkuan Square, Holkar University/IT Park, Rani Bagh, Limbodi, Ralamandal, Indore Bypass 1
Line-1B: Sri Aurobindo Hospital – Collectorate office – Regional Park (1B)
- Number of Stations: 13
- Station Names: Sri Aurobindo Hospital, Bhawarsala Square, Sanwer Industrial Area, Ganesh Sham Colony, Banganga, Laxmibai Nagar Square, Mara Mata Square, Imli Bazar Chowk, Rajwada Palace, Collectorate Office, Central Excise, Choithram, Regional Park
Line-2: Dewas Naka – Juni Indore – MHOW
- Number of Stations: 28
- Station Names: Dewas Naka, Niranjanpur Circle, Aranya Nagar, IDA Park, Vijay Nagar Square, Bhamori, Patni Pura/St Joseph Church, Malwa Mill Square, Raj Kumar Bridge, Indore Railway Station, Juni Indore, Collectorate Office, Mhow Naka, Dusshera Maidan, Annapuran Temple, Narmada Public School (Ring Road), Rajendra Nagar, Reti Mandi, IPS Academy, Shramik Colony, Indore Bypass-2, Pigdambar, Umariya, Maa Vaishanodevi Hospital, Haranyakheri / IIT Indore, Chinar Residency, MHOW
Line-4: MR9 – Indore Railway Station – Indore Bypass 4
- Number of Stations: 16
- Station Names: MR9, Convention Center, Lahiya Colony, Chandragupta Square, Sukliya, Nanda Nagar Main Road, Mazdoor Maidan, Rajkumar Bridge, Indore Railway Station, Chhavani, Sri Agrasen Maharaj Chowk, Navlakha Bus Station, Teen Imli, Babul Nagar, Musakhedi, Indore Bypass 4
Progress on Indore Metro Rail Project
1. MPMRCL MD conducts Trolley Trials
On August 6-7, Mr. S. Krishna Chaitanya, Managing Director of Madhya Pradesh Metro, conducted a trolley trial from SC-02 to Malviya Nagar and performed an on-site inspection at the Indore Metro Gandhi Nagar Depot and the Priority Corridor. He issued directives to ensure the timely completion of the ongoing work.

Impacts of Indore Metro
3. Streamlined Urban Mobility
The Indore Metro Project is designed to strengthen urban mobility by creating direct transit linkages between major nodes such as educational institutions, healthcare facilities, employment hubs, and commercial zones. By integrating these high-demand areas into a structured mass transit network, the system will facilitate predictable and time-efficient travel across the city.
2. Mitigation of Traffic Congestion
The commissioning of the Super Priority Corridor of the Indore Metro is expected to reduce vehicular load on arterial roads and intersections. The Indore metro system provides an incentive for modal shift from private vehicles to public transit by offering a high-capacity, reliable, and scheduled transport alternative, thereby contributing to more balanced traffic distribution within the urban road network.
3. Economic and Developmental Impact
The Indore Metro is anticipated to generate positive economic externalities by enhancing intra-city connectivity and improving accessibility to key commercial and industrial clusters. The project will not only support employment generation during construction and operations but also facilitate transit-oriented development (TOD) along the metro corridors, that will encourage investment in real estate, retail, and service sectors.
4. Ridership Concern
- Ridership level remains a major concern for the Indore Metro project despite the launch of its super-priority corridor. The 5.9 km corridor began commercial operations on June 1, 2025, and carried 26,803 passengers on its first day. However, daily ridership dropped sharply to just 680 by July 1, which indicates a decline of 97.46%. This sharp decline in ridership raises concerns about the long-term sustainability of the project.
Conclusion
The Indore Metro outlines a transformative phase in the city’s urban development, aiming to address the challenges posed by rapid population growth and traffic congestion. The under-construction Indore Metro Project, developed by MPMRCL, marks a major step in modernizing the city’s urban transport. Phase 1 consists of one metro corridor, which spans 33.53 km. Recently, Prime Minister Narendra Modi inaugurated the Super Priority Corridor of Indore Metro in May 2025. The Indore metro project aims to improve connectivity and reduce traffic congestion in the city. However, challenges like fluctuating ridership levels remain a major concern for the authorities. Addressing these issues will be essential to ensure the long-term success and transformative impact of the Indore Metro on the city’s urban mobility.








