Introduction
Indian Railways is a state-owned enterprise under the Ministry of Railways, Government of India, and operates the country’s national railway system. The idea of Indian Railways was first proposed in 1832 in Madras. The Indian Railways is the fourth largest network in the world in terms of size. It has a total track length of 132,310 kilometres (82,210 miles). The running track length is 106,493 kilometres (66,172 miles), and it covers a route length of 68,584 kilometres (42,616 miles).
Indian Railways has not only enhanced the movement of people but has also made the transport of goods more convenient thereby reducing the logistic cost.
India’s Efforts in Millennial Railways refers to modernising and transforming India’s railway system to meet the demands of the 21st century, catering to technological advancements, growing passenger numbers, sustainability, and future-ready infrastructure. Millennial Railways emphasises the need to adapt Indian Railways to the expectations of modern society, with a focus on innovations, technology, speed, and efficiency.
Efforts by India to Modernise the Indian Railways
The Indian Railways has been putting striking efforts to modernise and upgrade one of the world’s largest railway networks. Over the years, the Indian Railways has taken major initiatives to enhance safety, improve passenger services, and advance infrastructure. This article reflects the key elements driving the modernisation of Indian Railways:
Increased Capital Expenditure
In the last decade, Railways’s Capital Expenditure has increased substantially. It grew from Rs 93,520 crore in 2015-16 to Rs 2,65,200 crore in 2024-25. This is an annual growth rate of 12%. The central government grants and additional borrowing have financed this increase.
- Technological Upgrades
The Indian Railways has been introducing and implementing a wide range of technological upgrades to enhance the efficiency of the operation by real-time monitoring of trains and train tracks. Moreover, the integration of technology in the railway system has also contributed in improving the passengers’ experience by providing services like automated ticketing systems and real-time updates about the trains. Some of the major technological revolutions that contributed to modernising the railway systems are mentioned below:
1. Digitalisation and Automation: Indian Railways, one of the largest railway networks globally, is undertaking a major initiative towards digitalisation and automation of railway systems to modernise operations and enhance passenger services. Some major initiatives by railways towards digitalisation and modernisation are:
- Introduction of Advanced Signalling System: The most critical step taken by the Indian Railways is the introduction of advanced and modern signalling systems. These systems utilise technologies which contribute to the effective management of operations.

- For example, the automatic block signalling (ABS) system is deployed on railways, and the movement of the trains is controlled by automatic stop signals, preventing trains’ collisions.
- GPS and Tracking Systems: Another major step taken by Indian railways towards modernisation is the adoption of GPS-enabled tracking systems. The Global Positioning System (GPS) technology provides real-time data about trains. Train tracking permits the railway operator to monitor the location and speed of trains accurately. This data allows the operator to schedule the trains, ensuring that they operate on time.
- Online Ticket Booking System: One of the major technological adoptions is the computerised reservation system that Indian Railways has implemented to enhance passengers’ experience. Through this, commuters can purchase reserved or unreserved train tickets, cancel train tickets and claim refunds online at any time according to their convenience.
- One India – One Ticket Initiative: The Indian Railway Catering and Tourism Corporation Limited (IRCTC), Delhi Metro Rail Corporation (DMRC) and Centre For Railway Information Systems (CRIS) joined hands to promote the ‘One India – One Ticket’ initiative, streamlining the travel experience for Main Line Railway and Metro passengers in the Delhi NCR area.
- Collaboration with NCRTC: Indian Railways and the National Capital Region Transport Corporation (NCRTC) have collaborated to provide passengers with a convenient travel experience. This collaboration allows travellers to seamlessly book and use both Indian Railways and Regional Rapid Transit System (RRTS) services.
- Digital platforms for Real-Time Updates: The Indian Railways has improved the efficiency and convenience of travel by creating several digital platforms which provide passengers with real-time updates about the trains.
- For example, RailYatri is an app and website which provides real-time information about the train’s positions, delays and train arrival times.
2. Infrastructure Development
In order to modernize operations, increase safety, and improve passenger facilities, Indian Railways is implementing a number of important infrastructure development projects. The following are the main projects that are underway at the moment:
1. Amrit Bharat Station Scheme: The Amrit Bharat Station Scheme aims to modernize railway infrastructure stations throughout the Indian Railways network. Under this scheme, a total of 1, 337 railway stations have been identified for redevelopment to improve passengers’ amenities and services.

- Several stations like Rani Kamlapati Station and Gandhinagar Capital Station have been redeveloped so far and are currently operational.
- Meanwhile, Indian Railways has already started work on 1,198 stations out of 1,337 stations under the Amrit Bharat Station Scheme.
2. Introduction Of Dedicated Freight Corridors: The share of railways in freight traffic dropped from 83% in 1950-51 to 35% in 2011-12. To increase this share, railways started a plan to build Dedicated Freight Corridors (DFCs) in 2005. It is intended to increase the effectiveness and speed of goods transportation by constructing railway lines that are only used for freight traffic.

Eastern & Western Dedicated Freight Corridors (DFC)
| Corridor | Length (km) |
| Eastern DFC | 1,337 |
| Western DFC | 1,506 |
| Total Length (excluding Sonnagar-Dankuni) | 2,843 |
Completion Target: December 2025.
Current Status of Western Dedicated Freight Corridor
| Section/Package | Length (km) | Commissioning Date | Financial Progress |
| Dadri – Rewari | 127 | 25.01.2024 | 93% |
| Rewari – Madar | 306 | 07.01.2021 | |
| Madar – Palanpur | 353 | 18.06.2022 | |
| Palanpur – Makarpura | 290 | 30.09.2022, 30.10.2023 | |
| Makarpura – Sachin | 135 | 12.03.2024 | |
| Sachin – Vaitarna | 193 | Commissioned | |
| Vaitarna – JNPT | 102 | To be Commissioned on 31.12.2025 |
Current Status of Eastern Dedicated Freight Corridor
| Section/Package | Length (km) | Commissioning Date | Financial Progress |
| Sahnewal – Pilkhani | 179 | 12.03.2024 | 95% |
| Pilkhani – Khurja | 222 | 12.03.2024 | |
| Khurja – Dadri | 46 | 25.01.2024 | |
| Khurja – Bhaupur | 351 | 29.12.2020 | |
| Bhaupur – DDU | 402 | 18.12.2023 | |
| DDU – Sonnagar | 137 | 07.07.2023 |
Note: Indian Railways loaded 1,473 MT of freight in 2024, achieving a 3.86% growth, with EDFC and WDFC facilitating over 72,000 train runs.
3. Electrification of Railway Tracks: The Indian Railways has been making continuous efforts towards enhancing railway track infrastructure in order to increase train running efficiency and support high-speed rail and freight transportation in India. The major step taken by Indian Railways in order to achieve this is the electrification of railway tracks.
- In Year 2024, a total of 3,210 route kilometres (RKM) were electrified, extending electrification to approximately 97% of the Broad Gauge (BG) network.
3. Passenger- Centric Services
Indian Railways’ top most priority is the passengers’ convenience and overall journey experience. In order to enhance the overall travel journey of Passengers, Indian Railways has been improving its infrastructure and striving hard to provide modernised and advanced amenities like wifi connectivity, and an online ticket booking system to commuters. Key initiatives and amenities introduced by Indian Railways to enhance overall passenger experience are mentioned below:
- Wi-Fi Connectivity: The Indian Railways has been providing passengers with free wifi facility at stations. Currently, Wi-Fi services are available at 6,112 stations across the Indian Railways network.
- Water Vending Machines (WVMs): To maintain the hygiene protocol the Indian Railways installed Water Vending Machines ( WVMs) at various stations to provide passengers with clean drinkable water.
- Installation of CCTV Camera: The safety of passengers is the main concern of Indian Railways. In response to this Indian Railways installed CCTV cameras at all stations (except halt stations).
4. Safety Measures and Innovations :
In the last decade, Railways’ Efforts to reduce train accidents and provide safer travel to passengers have been unparalleled. The organisation has implemented multiple initiatives that have established Railways as a safer mode of transportation for travellers.
The Key Initiatives Include
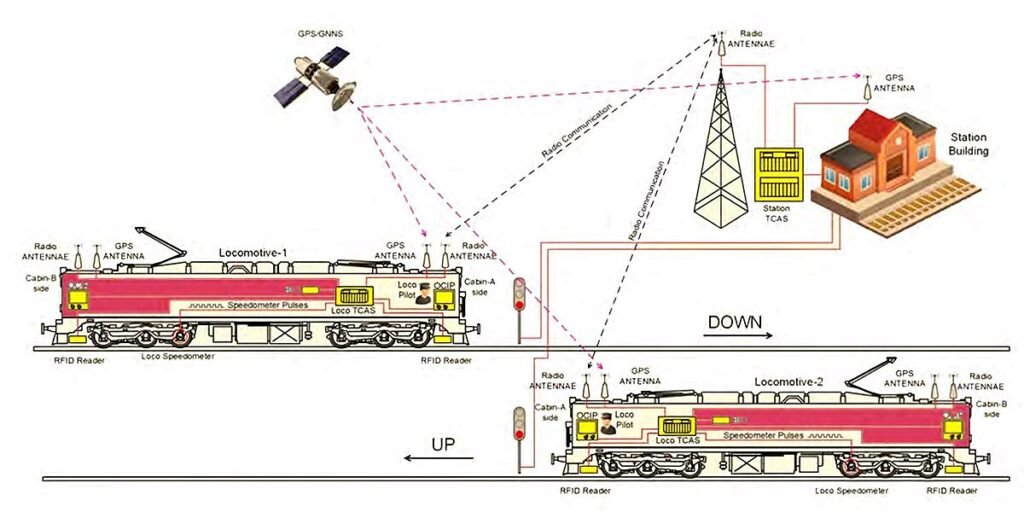
1. Deployment of Kavach System
Kavach is an Automatic Train Protection System (ATP), the thing that makes Kavach stand out among other safety systems is that it was developed indigenously by the Research Design Standard Organisation in collaboration with Medha Servo Drives, Kernex Microsystems and HBL Power Systems. The cost for the Track Side and Station equipment of Kavach is about Rs. 50 Lakhs per kilometre, while the cost for Kavach equipment on locomotives is around Rs. 80 Lakhs per locomotive.
- Railways aims to equip 10,000 locomotives with Kavach in the coming years.
- To facilitate the Kavach installation Railways is preparing 69 loco sheds.
- Working Mechanism
It’s a high-tech system that meets the highest safety standards (SIL-4). Its main purpose is to prevent trains from passing a red signal, which indicates danger, and to prevent collisions. If the driver doesn’t manage the train’s speed properly, the system can automatically activate the brakes. The system also helps prevent crashes between two trains that have the system installed.
- Progress on the Kavach System
| Aspect | Details |
| Funds Utilized (so far) | ₹1,547 Crores |
| Allocation of Funds (2024-25) | ₹1,112.57 Crores |
| Kavach Version | Version 4.0 (Approved by RDSO on 16.07.2024) |
| Deployment Completed | 1,548 RKm (South Central & North Central Railway) |
| Current Work in Progress | Delhi–Mumbai & Delhi–Howrah corridors (~3,000 RKm) |
| Trackside Works Completed | 1,081 RKm |
| Trackside Works Details | – 705 RKm (Delhi–Mumbai section) |
| – 376 RKm (Delhi–Howrah section) |
Comparative Analysis of Track Maintenance Enhancements:
2004-14 vs. 2014-24
| Item | 2004-05 to 2013-14 | 2014-15 to 2023-24 | 2014-24 Vs. 2004-14 |
| Expenditure on Track Renewal (₹ in Cr.) | 47,038 | 1,09,577 | 2.33 times |
| Rail Renewal Primary (Track Km) | 32,260 | 43,335 | 1.34 times |
| Use of high-quality rails (60 Kg) (Km) | 57,450 | 1,23,717 | 2.15 times |
| Longer Rail Panels (260m) (Km) | 9,917 | 68,233 | 6.88 times |
| USFD (Ultra Sonic Flaw Detection) Testing of Rails (Km) | 20,19,630 | 26,52,291 | 1.31 times |
| USFD (Ultra Sonic Flaw Detection) Testing of Welds (Nos.) | 79,43,940 | 1,73,06,046 | 2.17 times |
| New Track KM added (Track Km) | 14,985 | 31,180 | 2.08 times |
| Weld Failures (Nos.) | 2013-14: 3,699 | 2023-24: 481 | 87% reduction |
| Rail Fractures (Nos.) | 2013-14: 2,548 | 2023-24: 383 | 85% reduction |
| Thick Web Switches (Nos.) | Nil | 21,127 | – |
| Track Machines (Nos.) | As of 31.03.14: 748 | As of 31.03.24: 1,661 | 122% increase |
Signalling and Rolling Stock Enhancements: 2004-14 vs. 2014-24
| SN | Item | 2004-05 to 2013-14 | 2014-15 to 2023-24 | 2014-24 Vs. 2004-14 |
| Signaling Works | ||||
| 1 | Electronic Interlocking (Stations) | 837 | 2,964 | 3.52 times |
| 2 | Automatic Block Signaling (Km) | 1,486 | 2,497 | 1.67 times |
| 3 | Fog Pass Safety Devices (Nos.) | As on 31.03.14: 90 | As on 31.03.24: 19,742 | 219 times |
| Rolling Stock | ||||
| 1 | Manufacture of LHB Coaches (Nos.) | 2,337 | 36,933 | 15.80 times |
Paradigm Shift Towards Green Energy
Indian Railways is committed to achieving net-zero emissions by the year 2030. In alignment with this goal, the organization is actively employing renewable energy sources to fulfil its power supply requirements.
| Renewable Energy Source | Capacity (as of November 2024) | Description |
| Solar Power | 487 MW | Includes both rooftop and ground-mounted solar power plants commissioned by Indian Railways. |
| Wind Power | 103 MW | Wind power plants are installed to contribute to renewable energy generation. |
| Renewable Energy – Round the Clock (RE-RTC) | 100 MW | 100 MW of RE-RTC began supplying continuous renewable energy. |
| Total Renewable Capacity Tied Up | 2,014 MW | Total secured renewable energy capacity, covering various sources including solar, wind, and RE-RTC. |
Development of High-Speed Rail Corridor
The Mumbai- Ahmedabad High-Speed Rail Corridor is India’s first high-speed rail corridor. The National High-Speed Rail Corporation Limited (NHSRCL) is implementing this 508 km long project at an estimated cost of Rs. 1,08,000 crore. The first section, spanning 50 km between Surat and Bilimora of this corridor, will become operational by August 2026 as mentioned by Railway Minister Shri Ashwini Vaishnaw. The remaining corridor will be opened between 2028 and 2030. The corridor is designed for bullet trains running at a maximum speed of 320 kmph. The significance of this project lies in the fact that the MAHSR corridor will reduce travel time between the two economic hubs, Ahmedabad and Mumbai, from the current 7 hours to just 2 hours.
Modern Trains: Giving Edge to Rail Transportation
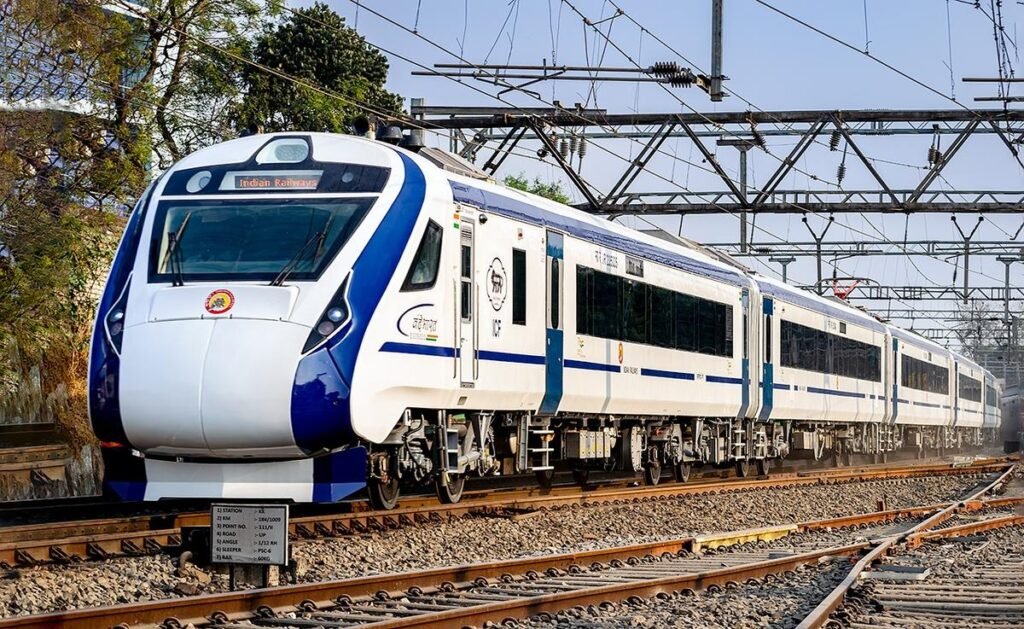

To make journeys more comfortable, smooth, fast and safe, IR has taken various initiatives and one of them is developing smart trains that can provide a better travel experience at affordable costs. In recent years Railways has launched the following trains:
- Train 18
Initially known as “Train 18”, Vande Bharat Train became the first semi-high-speed train in India that was manufactured indigenously aligning Indian government’s Make in India initiative. The Vande Bharat is also the fastest train in the nation as it can run at a maximum speed of 180 kmph. The first Vande Bharat train ran on February 15, 2019, on the New Delhi-Kanpur-Allahabad-Varanasi route. Currently, Indian Railways is operating 136 Vande Bharat trains running across the country on medium & short distances. Union Minister Shri Jyotiraditya Scindia said that there will be 4500 Vande Bharat Trains in India by 2047.
- Vande Bharat Sleeper Train
India’s first sleeper version of Vande Bharat is gearing up for the launch. The Research Design Standard Organisation conducted multiple trials in January 2025. During the trials, the Vande Bharat sleeper train achieved a peak speed of 180 km per hour in a 40 km long trial run between Rohal Khurd to Kota.
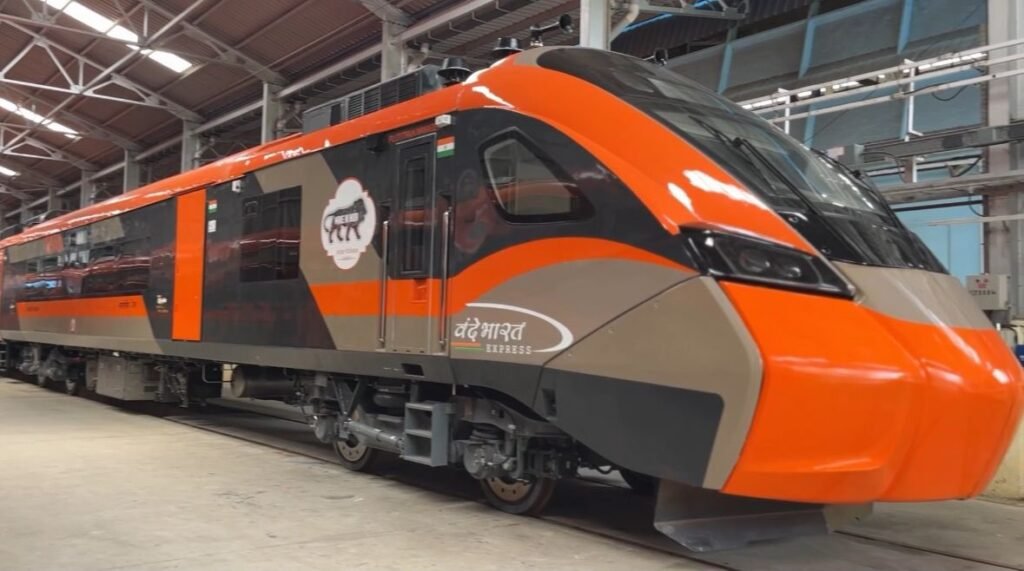

- Namo Bharat Rapid Rail (Vande Metro)
To enhance connectivity between cities Indian Railways launched Vande Metro. The train was renamed Namo Bharat Rapid Rail. The train was initially launched between Bhuj and Ahmedabad.
| Features | Details |
| Number of Coaches | 12 |
| Seating Capacity | 1,150 passengers |
| Maximum Speed | 110 km/h |
- Amrit Bharat Train Services:
Amrit Bharat services provide quality travel with non-AC trains. Each train has 12 Sleeper Class coaches and 8 General Class coaches. In 2024, two new Amrit Bharat Express services were launched: the Darbhanga–Anand Vihar (T) Express and the Malda Town–SMVT Bengaluru Express. More services are planned for the future.
Conclusion
Indian Railways is using a multifaceted approach to support the growth of nation. With increased budgetary assistance from the central government, railways is not only upgrading its infrastructure but also striving to provide an efficient mode of transport to its passengers at affordable prices. The electrification of 97% of the broad gauge network, commissioning of 2,843 km of Dedicated Freight Corridors, and introduction of advanced safety systems like Kavach highlight these efforts. With ₹2.65 lakh crore allocated in 2024-25 for infrastructure and technological upgrades, Indian Railways is steadily progressing toward a more sustainable and efficient future, aligning with global railway standards while addressing the growing demands of freight and passenger transport.





