The evolution of bogies and wheelsets over the past decades has been marked by notable progress, driven by a combination of several key factors. Bogies and wheelsets have transformed over time, getting better and stronger. They help trains run smoothly and safely on the tracks, making sure everyone gets where they need to go. The advancements are admirable and we should take a closer examination to distinguish their efficacy and potential for further improvement.
One crucial aspect of this transformation has been the pursuit of lightweight design and the integration of best materials. They’ve changed a lot over the years, becoming lighter and stronger. This helps trains move faster and more efficiently. In response to the critical need for improved energy efficiency and reduced operational burdens, the exploration and adoption of materials such as high-tensile steel and carbon fiber reinforced plastics (CFRP) have been instrumental. By adopting these materials for bogie frames, weight is reduced by 40-50% substantially. However, while these endeavours represent commendable progress, there remains room for crucial evaluation regarding the durability and cost-effectiveness of these lightweight solutions.
The introduction of computational simulation and advanced assessment methodologies has shown a new era of design suitability. These sophisticated tools have enabled the use of lightweight materials without compromising structural strength. Nevertheless, a careful inspection is required to ensure that the promises of these methodologies transform into visible benefits without sacrificing safety or reliability.

The era of digitalisation has penetrated every aspect of train engineering in the hope of efficient and optimized functioning. The rise of digital twins, virtual tests and data-driven maintenance, all boosted by machine learning and artificial intelligence, marks a big change in how things are done. Yet, as we embrace these technological marvels, we need to carefully examine whether these ideas actually work in real life and if there are any problems we might not see at first. Otherwise, we might get caught up in new ideas without really getting any benefits from them.
Steps towards automation and manufacturing have posed both opportunities and challenges. The integration of highly automated robotic lines into production processes holds promise for streamlining operations and enhancing productivity. But making sure the welding works and everything is easy to reach in these automatic systems is really tricky. We have to be really vigilant and check everything closely to avoid unexpected problems.

Looking ahead, the trajectory of the Train Bogies market appears promising, with a great emphasis on sustainability and technological integration. However, as we follow this journey of progress, it is important to maintain an observant stance, critically evaluating each step to ensure that innovation aligns harmoniously with practicality and efficacy. The upcoming decade holds immense potential for growth, followed by ambitious initiatives like the Indian government’s plans for rail corridor expansion. Yet, it is only through a judicious blend of positivity and critical inspection that we can navigate this path and figure out how to make the most of new train technology.
Historical Glance – Evolution Over the Years
The journey of rail carriages is as fascinating as it is extensive. From the humble beginnings of basic designs lacking even fundamental amenities to the introduction of ultra-modern air-conditioned coaches, the trajectory of development reflects a constant pursuit of passenger comfort and safety. Rail travel has undergone a remarkable transformation, evolving from a basic and uncomfortable experience to a mode of transportation characterized by comfort and efficiency, all thanks to the evolution and historical development of bogies and trainsets.
Dating back to the early days of rail travel in India, many rail systems emerged, serving both commoners and royalty alike. While ordinary coaches served the masses, luxurious salons decorated with lavish furnishings served the elite, highlighting the clear difference in travel experiences.. However, as rail networks expanded and technology progressed, a gradual refinement in design and construction became evident.
The transition from timber to steel for underframes not only improved durability but also prolonged the lifespan of coaches, offering a sneak peek into the continuous pursuit of innovation within the industry. A firm commitment to safety and passenger comfort has remained at the forefront of industry priorities. The inclusion of stainless steel in coach construction, known for its resilience and impact-absorbing properties, aligns with the pursuit of safety standards.
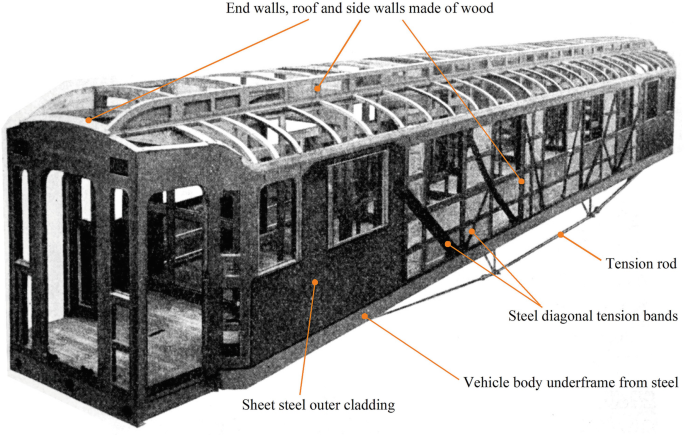
The introduction of bogie carriages in the early 20th century promised a new era of mobility characterized by improved stability and comfort. Yet, challenges persisted, with safety concerns due to inadequate braking systems and old lighting arrangements. However, innovations such as the vacuum brake and gas lighting represented enhanced passenger safety and convenience.
The post-war era proved to bring an upgrade with the adoption of all-metal lightweight carriages, a fusion of technology, and design ingenuity. The establishment of the Integral Coach Factory (ICF) in Perambur marked a turning point, facilitating the mass production of modern coaches designed to meet the evolving needs of passengers.

Today, as we reflect on rail history, the legacy of innovation and progress is evident. The Regional Rail Museum in Perambur stands as proof of this journey, showcasing a treasure collection of coaches that witnessed the evolution of rail travel.
India – Tracing the Bogie Journey
The train bogie plays a vital role in ensuring smooth and safe train operations. Positioned beneath the train, it attaches the wheels to the railway vehicles securily. Equipped with suspension and brake systems, the bogie ensures flexibility and comfort throughout the journey. It not only maintains the train’s quality but also guides it along the track, offering a multifaceted approach during operation. Crafted to fit the train’s structure and engine, it has proved to be a cost-effective transportation solution.

India’s railway journey initiated in 1832 when the first proposals for railways were made in Madras, setting the stage for a new era of transportation. The inaugural train journey in India, from Red Hills to Chintadripet Bridge in Madras in 1837, was powered by the innovative efforts of visionaries like Sir Arthur Cotton and William Avery.
The evolution of locomotive standards in India took a significant leap forward in 1924 with the formation of the Locomotive Standards Committee. This committee, tasked with updating and standardizing locomotive designs, recommended the adoption of Indian Railway Standards (IRS) classes, which included six broad gauge classes: XA (Branch line passenger-4-6-2), XB (Light passenger 4-6-2), XC (Heavy passenger 4-6-2), XD (Light Goods 2-8-2), XE (Heavy Goods 2-8-2), and XT (Light Tank 0-4-2 T). These standards not only transformed locomotive design but also paved the way for greater efficiency and performance across India’s railways.
Trivial Facts -Some key findings and developments over the years:
- The first three decades of the 19th century saw intensive manufacturing activity in railway workshops and local units.
- By 1880, the Indian railways owned 6,600 carriages, and by 1951, the number had gone up to 20,767 (excluding Pakistan).
- A third-class coach with a timber body cost Rs.1.25 lakhs in 1950.
- HAL produced 150 coaches a year during the Second World War when coach building was not easy.
- The introduction of Stainless steel coaches post-Second World War to absorb shocks of collisions and derailments, reduced rail accidents by one-fifth from 1960-61 to 2000-01.
- Tests have shown that austenitic stainless steel (S30103 and S30153) absorbs 2.5 times more energy during deformation than carbon and aluminium.
- The Integral Coach Factory (ICF) in Perambur was established in 1952, and in one year, it came out with over 1,000 drawings required to guide manufacturers on machinery and technicalities.
Innovative Design and Material Advancements
Newer, lighter materials like strong steel and special plastic have made train frames much lighter by about half! This means trains can use less energy and be more eco-friendly.
Harnessing the Power of Digitalization
Exploring the powers of digital twins, virtual data, and condition-based maintenance, added by machine learning and AI, not only accelerates time-to-market functioning but also regulates system availability and presents sustainable operations. Let’s understand this concept with the help of an example: imagine a company that makes cars. Instead of building physical prototypes of each car model, they use computers to create virtual versions. They also use special tests on these virtual cars to make sure they’re safe and meet regulations before they even build them. Plus, they use smart technology to keep the cars running smoothly, predicting when they might need repairs. This helps them get new cars to customers faster, ensures they work well, and it’s better for the planet too.
Automation and Manufacturing Progression
When we incorporate the powers of digital data along with the ‘Internet of Things’, we can make all the operations run in automatic mode as long as the conditions of machine learning are fulfilled. The use of robotics in manufacturing operations greatly reduces production time, leading to an increased production rate in a given time. This benefits not only the company but also meets the growing demands of present times. We especially need faster technology for repair systems, because it’s a machine, running non-stop, so we need quicker solutions so as to not halt its running progress.
Incorporation of Cutting-edge Technologies
The use of better technologies will no doubt help in the efficient functioning of any project. In this segment, we are talking about bogies and trainsets. With more and more development we would need our bogies to be as fast as possible, lightweight, able to withstand heavy loads, and more. Similarly in the trainsets, we would need the inclusion of facilities needed by an individual. So, when designing such models, we need good technologies to achieve smoother integration of upgrades.
Regional and Segment-specific Growth Dynamics
Population is growing and we also need better projects to replace the old segments, owing to sustainability. Indian government’s ambitious initiatives to develop new rail corridors and expand the existing track network by 40,000 km before 2030. It is thought to propel substantial demand for bogies and trainsets.
Global Outlook: Sustainability and Technological Integration
On a global scale, the concerted emphasis on environmentally sustainable solutions coupled with the continued integration of advanced technologies like AI and machine learning are set to steer the upward trajectory of growth in the Train Bogies market.
WHY? – Need to Upgrade Bogies and Trainsets
With changing times, we’ll need to upgrade all our models, in this case, bogies and trainsets. The demand in the present scenario is for safety, speed, and efficiency. In the global market, the train bogie sector is set out for growth, as the demand for safety in railway transportation increases. With a rising preference for public transit, particularly in recent times, this trend is expected to continue. Government regulations worldwide, emphasizing on passenger and cargo safety, will further fuel market expansion. Train bogies stand out for their energy efficiency and cost-effectiveness, making them a preferred choice in rail transport.
Types of Bogies
The design of bogies sets rail vehicles apart from their road counterparts. Initially, railway vehicles relied on fixed axles, but the introduction of the bogie, initially termed the “swiveling bolster,” revolutionized rail travel. A bogie, typically a short two or three-axle unit, is mounted beneath the vehicle frame, granting it a degree of freedom to move.
As locomotive technology evolved, movement power units predominantly adopted bogie designs, offering flexibility for passing curves seamlessly while maintaining radial flexibility through suspension mechanisms. However, smaller locomotives, shunters, and historic vehicles often retained fixed wheelsets. This showcases the diversity within the railway industry.
Each type of rail vehicle – locomotives, railcars, passenger coaches, freight wagons, underground, and suburban vehicles – features specific bogie designs tailored to meet specific requirements. These designs prioritize factors such as speed, comfort, load capacity, axle load, derailment safety, and smooth operation. The collection of bogie designs reflects the industry’s commitment to diverse performance across various operational contexts.
A notable feature of bogies is their ability to spin within the bogie frame mounted beneath the main frame of the vehicle. This pivotal movement is advantageous for several reasons:
- It enables the bogie to move in curves with greater ease, allowing rail vehicles to follow tighter curves, which was not possible with rigid wheelsets. Consequently, longer vehicles can be designed, limited only by the loading gauge profile in curves.
- Bogies absorb and control vertical and diagonal impacts on the track, reducing the forces transferred to the main frame by half. This mechanism contributes to smoother rides and minimizes wear and tear on railway tracks.
- Bogies distribute axle loads more evenly compared to individual axles, further reducing track wear and enhancing operational efficiency.
The innovative design of bogies represents a breakthrough in modern rail transportation, offering versatility, stability, and efficiency. As rail technology continues to evolve, bogie designs will undoubtedly play a pivotal role in shaping the future of rail travel, fostering a safer, more comfortable, and sustainable transportation ecosystem.
Two Axle Bogie
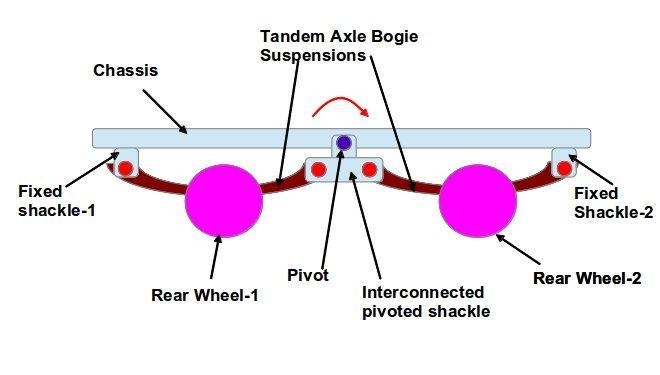
Two-axle bogies, characterized by a front and rear axle arrangement, are ideal for lighter vehicles like small trains, cars, and light trucks. Their design prioritizes motility and ride quality, making them key components of various transportation systems.
The hallmark of two-axle bogies lies in their ability to allow wheels and axles to move independently, enhancing steering responsiveness and overall driving experience. This independent movement translates into smoother cornering and better handling, crucial factors for vehicles navigating urban settings.
The versatility of two-axle bogies extends to commercial trains for passengers and metro systems, where they find applications in lighter rail vehicles such as commuter trains and tramcars. Their compact size and flexible performance make them well-suited for urban transit networks, facilitating efficient and comfortable travel for commuters
Three-Axle Bogies
On the other hand, three-axle bogies, featuring a front axle and two rear axles, are the workhorses of heavier vehicles such as freight trains,longer trains, trucks and light semi-trailers. Their strong design and structural complexity cater to the demanding requirements of heavy-duty transportation applications.
One of the primary advantages of three-axle bogies is their superior stability and load-bearing capacity. The additional axle enables these bogies to distribute weight more evenly, reducing strain on individual components and ensuring optimal performance under heavy loads. Moreover, three-axle bogies exhibit improved steering characteristics, thanks to their sophisticated design and engineering. This translates into improved handling and control, crucial for safely navigating challenging terrain conditions and tight spaces.
Three-axle bogies play a vital role in commercial trains for passengers and metro systems, particularly in locomotives (engines) and freight cars. Their robust construction and load-bearing capabilities make them essential for hauling heavy cargo and ensuring the smooth, reliable operation of rail services.
While two-axle bogies excel in agility and ride comfort for lighter vehicles, three-axle bogies offer unparalleled stability, load-bearing capacity, and steering precision for heavier applications. Together, these bogie arrangements transformed the base of transportation systems worldwide, contributing to efficient and sustainable mobility across transport industries.
Types of Trainsets – Commercial and Passenger Settings
Trainsets are commonly used in urban transit systems, commuter rail services, and high-speed rail networks, where they offer advantages such as faster acceleration, shorter dwell times at stations, and increased energy efficiency compared to traditional train design. Additionally, trainsets are often designed to be modular, allowing for easier expansion or modification of the fleet to meet changing operational requirements.
Key factors to consider for trainset development in commercial trains:
- Comfortable seating arrangements designed for long-distance travel.
- Optimal design for optimal support and relaxation during the journey.
- Well-equipped toilet modules with modern facilities for passenger convenience.
- Spacious interiors with ample legroom and storage space for luggage.
- Advanced air-conditioning systems for climate control and passenger comfort.
- On-board electronics for entertainment and communication purposes.
- Efficient passenger access products for seamless boarding and deboarding.
- Sunlight-readable displays for public information and advertising, enhancing the overall travel experience.
ICF Coaches to LHB Coaches
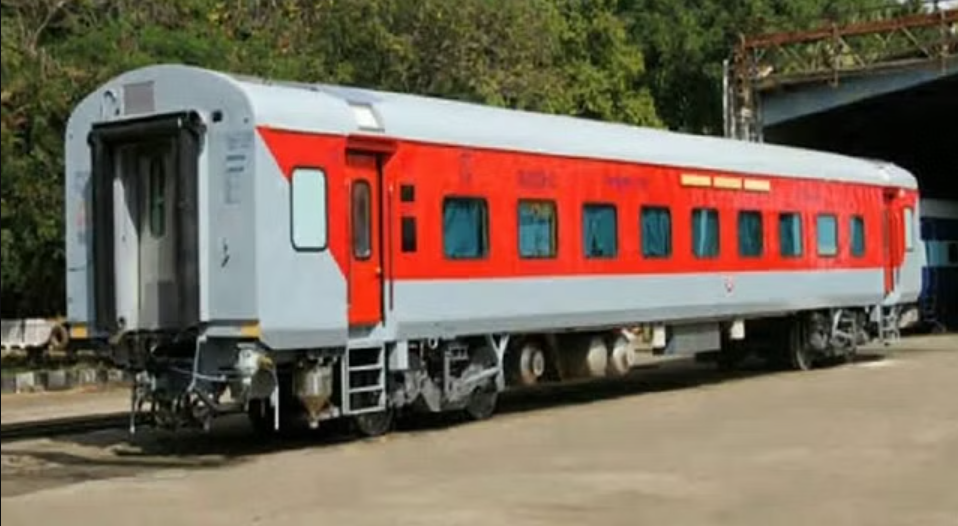

Indian Railways is swiftly upgrading its train fleet by replacing traditional Integral Coach Factory (ICF) coaches with modern and more advanced Linke Hofmann Busch (LHB) coaches. According to the Ministry of Railways, a remarkable total of 23,000 conventional ICF coaches have been effectively replaced by LHB coaches since 2015.
These LHB coaches have several advanced features, including an anti-climbing arrangement, secondary air suspension, corrosion-resistant shell, and improvised ride quality, ensuring safer and more comfortable journeys for passengers. The decision to discontinue the manufacturing of ICF coaches from FY 2018-19 onwards remark the national transporter’s commitment to technological growth and passenger satisfaction.
Notably, the LHB coaches have seen a significant increase in production in recent years. In the last financial year alone, the national transporter manufactured an impressive 4,175 LHB coaches (until January 31, 2023). Of these, 1,221 coaches were produced at Rail Coach Factory (RCF), 1,891 at Integral Coach Factory (ICF), and 1,063 at Modern Coach Factory (MCF). This represents a remarkable 45 percent increase in LHB coach production compared to the previous financial year.
The production trend reflects the steady growth in the adoption of LHB coaches by Indian Railways. With 4,429 coaches manufactured in FY 2018-19, followed by 6,277 coaches in FY 2019-20, 4,323 coaches in FY 2020-21, and 6,291 coaches in FY 2021-22, the upward trajectory marks the railways’ relentless efforts towards modernization and enhancement of passenger amenities.
Vande Bharat
This is a flagship semi-high-speed trainset introduced by Indian Railways. It operates between major cities like Delhi and Varanasi, offering modern beneficiaries and a comfortable travel experience.
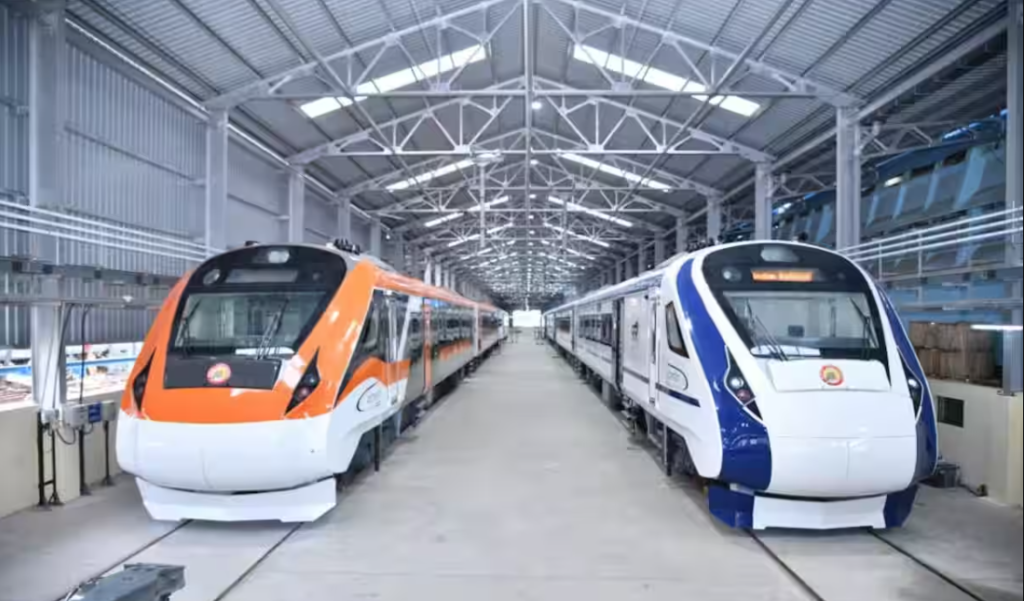

Features
- High Speed – In 2022, the second-generation trains set a new speed record, accelerating to 100 km/h (62 mph) in just 52 seconds, compared to the previous version’s 54 seconds. Additionally, these trains reached a speed of 160 km/h (99 mph) in 140 seconds, 5 seconds faster than their predecessors.
- Light–weighing 392 tonnes compared to 430 tonnes, and features larger 32-inch television screens and onboard Wi-Fi.
- The air conditioning system on the VB2 trains uses 15% less energy than the first generation, and they come equipped with automatic plug doors, emergency communication units, and accessible toilets.
- Bigger driver’s cabin and seats that can be reclined smoothly with a push-back arrangement.
- For safety, the VB2 trains are fitted with Kavach signaling technology, Fibre Reinforced Polymer (FRP) seats, and various emergency features including emergency windows, disaster lights, fire survival cables, and ventilation for up to three hours in case of power failure.
- The Kavach system activates the train braking system automatically if the driver fails to control the train according to the speed, thereby preventing collisions between two locomotives equipped with a functional Kavach system.
- Centralized Coach Monitoring System for electricity and climate control.
- Furthermore, the VB2 trains are equipped with a bacteria-free air conditioning system and enhanced flood protection for electrical equipment, ensuring reliability during monsoons up to 65 cm (26 in).
On 24 September 2023, 9 new Vande Bharat Express trains were introduced with upgraded features based on passenger feedback, including improvements in seats, toilets, and an advanced aerosol-based fire detection and suppression system.
Humsafar Express
Indian Railways, under the leadership of Suresh Prabhu, has invested Rs 20 lakh per coach to upgrade the Humsafar Express, intending to elevate passenger comfort. The revamped features include baby seats in toilets, comfortable side berth seats, reading lights, and USB charging points. One significant improvement is the redesigned side lower berth, addressing a long-standing complaint of passengers. A detachable board has been introduced to prevent backaches and enhance comfort during travel.
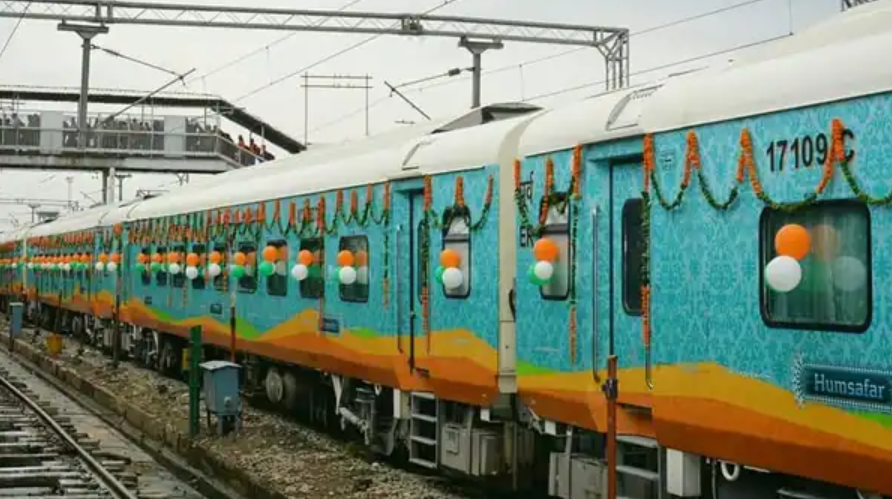

The interiors of the new Humsafar Express have been renovated, with changes in curtain design and lighter, fire-resistant curtains. USB charging points and reading lights have been installed next to each berth, while upper berth climbing arrangements have been made more convenient with added handles. In a family-friendly move, baby seats have been added in the toilets, aiding parents in changing diapers. Additionally, a sensor-based men’s urinal has been introduced, along with a two-step floor design for water containment.
The exterior features a reflective destination board and 3D numbering for easy identification, along with anti-graffiti coating. The train’s flooring has been upgraded with vinyl coating for easier cleaning. Despite these enhancements, ticket prices remain unchanged, a gesture appreciated by passengers. The Humsafar Express, with its improved amenities, aims to generate more revenue while providing better facilities to passengers, contributing to a more comfortable and enjoyable journey.
Tejas Express
The two versions of Tejas trains, one operating between Chhatrapati Shivaji Terminus (CSMT), Mumbai, and Karmali, are manufactured at Rail Coach Factory, Kapurthala, while the other running between Chennai Egmore and Madurai, are manufactured at Integral Coach Factory, Chennai. Designed for a maximum speed of 200 km/h (120 mph), the Tejas Express operates at an average speed of 65 km/h (40 mph) due to track and safety constraints.
Each Tejas Express comprises 14 non-executive chair cars, accommodating up to 72 passengers in a 3+2 configuration, and two executive chair cars with a seating capacity of 56 passengers each. The executive chair cars feature adjustable headrests, arm support, and leg support, while the non-executive chairs offer comfortable seating height.

The coaches are equipped with bio-vacuum toilets, water level indicators, tap sensors, hand dryers, integrated braille displays, LED TVs for each passenger with phone sockets, local cuisine, celebrity chef menu, WiFi, tea & coffee vending machines, magazines, snack tables, CCTV cameras, and fire & smoke detection and suppression system.
Fares for the Tejas Express are typically 20% to 30% higher than those of Shatabdi trains. The coaches feature redesigned seats with eco-leather, soap dispensers, touchless water taps, odor-control systems, occupancy indicators, and centrally controlled doors. Other amenities include large windows, electric outlets, overhead racks on chair car rakes, underneath storage on sleeper car rakes, automatic doors, smoke alarms, and sensor-based water taps.
Gatimaan Express
India’s inaugural semi-high-speed train, Gatimaan Express, capable of reaching speeds up to 160 km/h, operates between H. Nizamuddin and Agra Cantt. stations. The train is inaugurated by Railway Minister Shri Suresh Prabhakar Prabu, marking a significant milestone in India’s rail transportation.

Gatimaan Express introduces several enhancements to the passenger experience. On-board catering, managed by IRCTC, includes the deployment of train hostesses and offers a variety of cuisines. Additionally, passengers can enjoy complimentary entertainment via MyFreeTv.in without an internet connection through onboard WiFi.
The train features new LHB coaches from Rail Coach Factory, Kapurthala, equipped with bio-toilets, balanced draft gear couplers, soap dispensers, auto-genitors, and free microburst systems for improved hygiene. The coaches’ interiors boast scenic pastings and aesthetic upgrades, while the exteriors sport a fresh color scheme. The flooring receives a marathon Shine treatment for cleanliness.
Regulatory Measures and Sustainability
Implementing any project of such motive and vastness will need timely regulatory invasions to check on the operational progress. So many factors are being included, and with so many bigger organizations on board, the promise to present a great project is a critical task. Even the public has high hopes and is in alignment with the government’s initiative. Thus presenting regular reports and keeping records can help officials keep track of measures that are being opted critically.
The Government of India, in alignment with its Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs), has committed to reducing emissions intensity by 33%, with a particular focus on the transport sector. Indian Railways’ use of renewable energy sources in its energy mix is expanding. They are improving energy efficiency in both diesel and electric friction systems to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. The implementation of the Perform, Achieve, and Trade (PAT) Scheme in the railway sector, the introduction of a 5% blend of biofuels in traction diesel fuel, and the improvement of water use efficiency by 20% by 2030 are among the other measures being undertaken. Initiatives such as increasing carbon sink through extensive tree plantation, waste management, pollution control measures, and adoption of green practices in infrastructure development contribute significantly to environmental sustainability. Active participation in the Swachh Bharat Mission and working towards achieving a “Net Zero” status by 2030 through complete electrification of railway tracks further underscore Indian Railways’ commitment to sustainable development and mitigating climate change. Through these concerted efforts, Indian Railways is not only contributing to mitigating climate change but also spearheading sustainable development in the transport sector.
Conclusion
The evolution of bogies and trainsets over the years has been remarkable, driven by a commitment to safety, reliability, energy efficiency, speed, aesthetics, and cargo management. From the early proposals for railways in the 19th century to the introduction of high-speed trains and advanced bogie technologies, the journey has been marked by continuous innovation and adaptation. The concept of upgrading is essential to keep pace with evolving needs and technological advancements. Different types of bogies have been developed to cater to diverse requirements, whether for cargo movement or passenger journeys, spanning long distances or short commutes. These variations offer flexibility and customization options, ensuring optimal performance and comfort for various travel purposes. Additionally, the introduction of different trainsets provides passengers with a range of choices based on preferences, offering enhanced amenities and services to meet varying needs.
Sustainability has emerged as a crucial consideration in the development of bogies and trainsets. Efforts to enhance energy efficiency, reduce emissions, and incorporate eco-friendly materials highlight a collective shift towards green initiatives. By embracing sustainable practices and technologies, the rail industry is not only improving its environmental footprint but also contributing to broader sustainability goals. The ongoing advancements in bogies and trainsets underscore a commitment to innovation, safety, comfort, and sustainability. As the industry continues to evolve, embracing new technologies and practices, it remains poised to meet the growing demands of modern transportation while minimizing its environmental impact.








