Table of Contents
Introduction
Bhopal, the capital of Madhya Pradesh is the 16th largest city in India, famous for its history and cultural diversity. It was formed by Parmara King Bhoj in the 11th century.
The city has a diverse natural and artificial lake. Situated on the Malwa Plateau, just north of the Vindhya Mountain ranges, the city is famous for its diversified architecture. The city is considered one of the most crucial hubs within Madhya Pradesh. Bhopal serves as a home to numerous research and educational institutes and institutes of national importance in India namely IISER, MANIT etc. With that, the city hosts a variety of industries including automobile manufacturing, textiles, pharmaceuticals and electrical appliances.
Bhopal is also one of the greenest cities in India which reflects the city’s commitment toward sustainability. The city has been ranked as one of the Cleanest State Capitals of India for the last three years. However, major challenges arose in between this commitment when the city witnessed sudden population growth, leading to the increase in private vehicle ownership in the city. The increasing number of vehicles on the road of Bhopal increased the Air Pollution in the city.
The air quality of Bhopal became a major concern with the growing time. The Air Quality Index of the city was frequently indicating poor conditions. A recent report indicated that in 2023, for almost 140 days the AQI level of the city exceeded 300 on several occasions making the air unfit for breathing. Due to increasing urbanisation and deteriorating quality of air the city saw a need for a sustainable mode of transportation for the city like the Metro System. In September 2019 the Chief Minister of the state laid the foundation stone of Bhopal Metro.

Bhopal Metro Project
Overview
Bhopal Metro, also referred as Bhoj Metro is an under-construction Mass Rapid Transit System (MRTS) for the city of Bhopal by the Madhya Pradesh Metro Rail Co Limited (MPMRCL). The Phase 1 of the Bhopal Metro consists of 2 corridors with 28 stations in total. Phase 1 is expected to become operational by 2027.
May 2013: Rohit Associates Cities & Rails Pvt.Ltd was appointed to prepare the master plan for the Bhopal Metro Project. The master plan suggested a 105 km route with 6 corridors for Bhopal Metro out of which Lines 2 & 5 were identified for Phase 1.
December 2016: The state government approved the Detailed Project Report (DPR) of Phase 1 spanning 27.90 km.
October 2018: The DPR of Phase 1 with a route of 27.90 km was approved by the Central Government.
January 2019: The construction work on the Phase 1 of Bhopal Metro commenced.
September 2019: The Chief Minister of Madhya Pradesh laid the foundation stone of the Bhopal Metro and nicknamed it Bhoj Metro after Parmar King Bhoj.
Funding Mechanism
The Bhopal Metro Project is estimated to cost Rs. 6941.40 crores.
Loans
The project will be financed through a 400 million euro loan from the European Investment Bank (EIB) signed on December 20, 2019, and an official development assistance (ODA) loan from the Asian Development Bank (ADB).
| Note: In the fiscal year 2024, the Union Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs approved Rs 882 crore to the Bhopal Metro with an increase of Rs 269 crore from last year’s budget.Till now, the Union govt has allocated Rs 2239 crore for the Bhopal metro including this fiscal year. |

Key Specification
| Authorized Authority | Madhya Pradesh Metro Rail Co Limited (MPMRCL) |
| Speed and Track | Top Speed: 80 kmphAverage Speed: 34 kmphTrack Gauge: Standard Gauge – 1435 mm |
| Electrification | 750 V DC Third Rail |
| Signalling | Communications-Based Train Control (CBTC) |
| Project Cost | Rs. 6941.40 crores ( Approx) |
| Estimated Ridership | 2.20 lakh/day (2027) |

Contractor’s List
| Contract | Contractor |
| Preparation of Detailed project report (DPR) of Bhopal Metro | Rohit Associates Cities & Rails Pvt.Ltd |
| Package-01: Construction of Line-2’s 6.225 km viaduct from AIIMS to Subhash Nagar including entry/exit viaduct to the depot. | Dilip Buildcon Ltd. |
| BH-04: Construction of 3.39 km underground twin tunnels and 2 underground stations at Bhopal Junction Station and Nadra Bus Stand. | KPIL – Gulermak JV |
| BH-07: Ballastless Track (BLT) of Standard Gauge at Elevated and Underground sections along with Ballasted & Ballastless Track in Depot | Larsen & Toubro (L&T) |
| BH-IN-02: 156 Rolling Stock cars for Bhopal metros including Signaling and Train Control and Telecommunication Systems | Alstom |
| BH-05: Construction of 12.91 km Blue Line’s viaduct and 13 elevated stations | Afcons Infrastructure |
| BH-03: Construction of elevated viaduct and 6 stations between Subhash Nagar – Aish Bagh Ramp and Sindhi Colony Ramp – Karond Circle | URC Construction (Lowest Bidders) |
| BH-06: Construction of Subhash Nagar Depot | KEC – SAM JV (Lowest Bidders) |
| BH-02: Construction of 8 elevated stations on Line-2 between AIIMS – Subhash Nagar | URC Construction (Lowest Bidders) |
| BH-IN-21: Detailed Design Consultant for E&M works at : IN-04 (5 elevated stations) and IN-O5 (7 underground stations) on Yellow Line | Ayesa India (Lowest Bidders) |
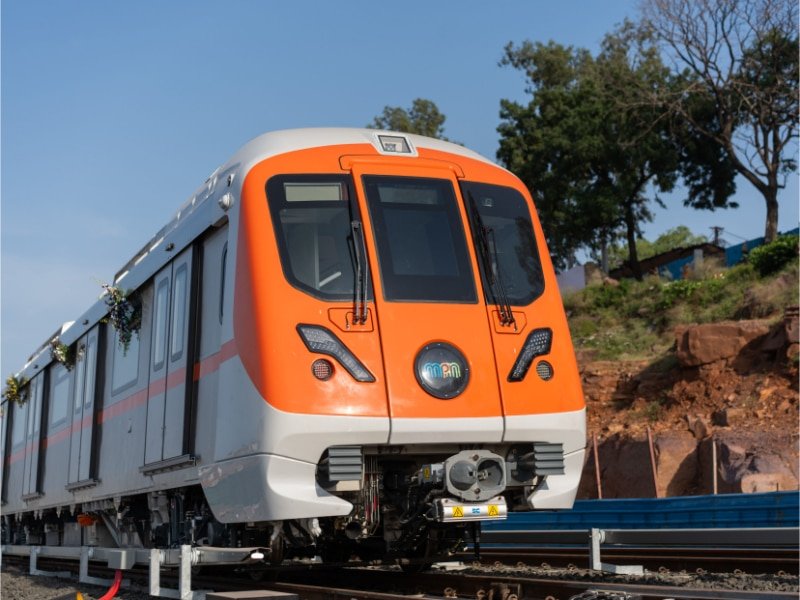

Rolling Stock
May 2022: Alstom grabbed Bhopal Metro’s rolling stock contract to supply and manufacture 27 trainsets (81 coaches) from MPMRCL.
March 2023: Alstom started the manufacturing of train sets in Savli, Gujarat. In
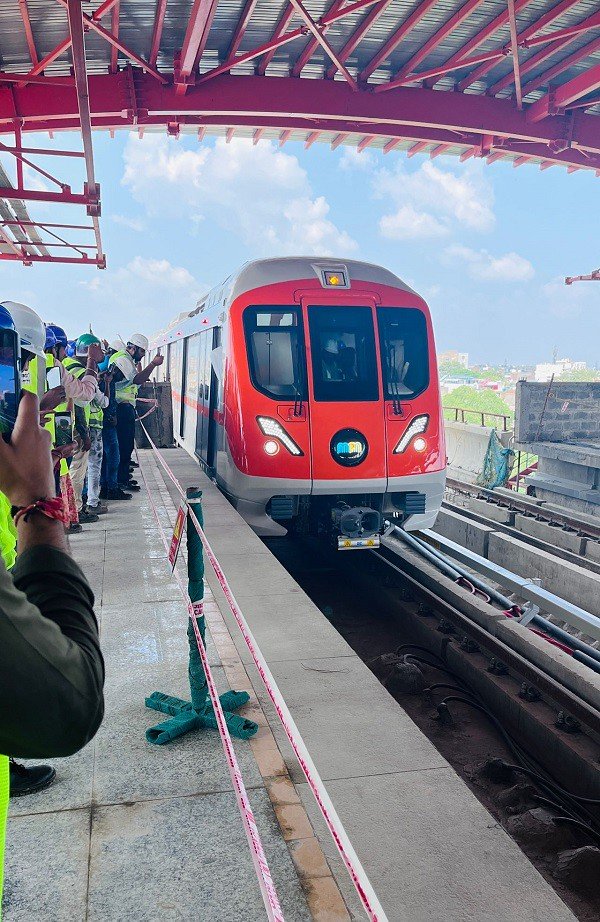
September 2023: Alstom delivered the first 3 coach train set for the Bhopal Metro at Subhash Nagar Depot.

| Updates: Train Trials In October 2023, MPMRCL conducted the trials of the first trainset delivered by Alstom. The trials took place between Subhash Nagar Depot and Rani Kamlapati Railway Station. Further Details: Out of 27 train sets, 14 trains will be operating on Line 2 from Karond Circle to AIIMS while the remaining 13 trains will be operating on Line 5 between Bhadbhada Square and Ratnagiri Tiraha. |

Status of Bhopal Metro
| Operational: | 0 km |
| Under Construction: | 6.22 km |
| Approved | 21.65 km |
| Proposed | 77.13 km |
Bhopal Metro Phase 1
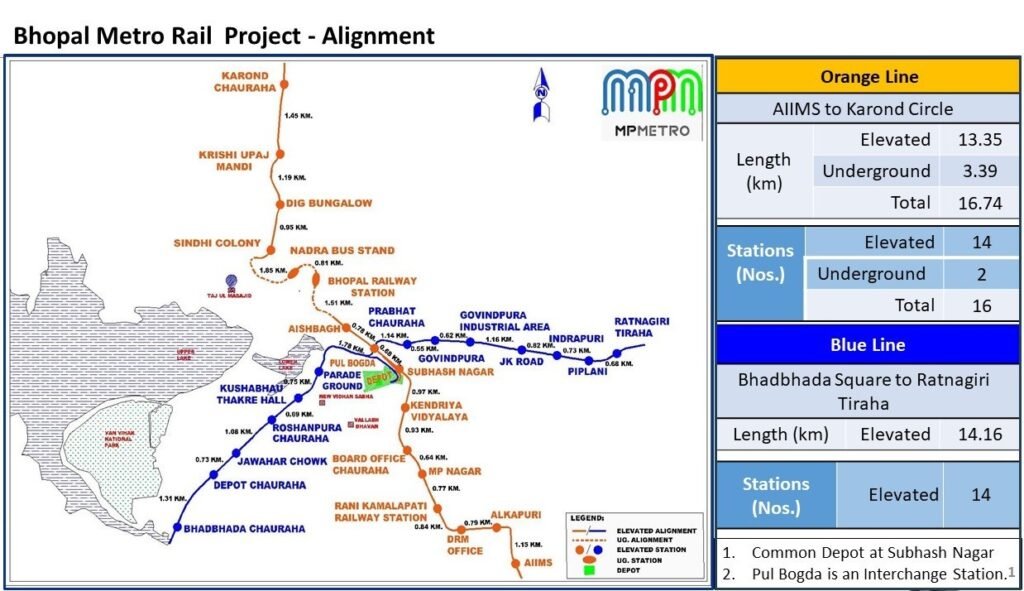
Line-2 (Orange Line): Karond Circle – AIIMS
- Length: 14.99 km
- Type: Elevated & Underground
- Status: 6.225 km is under construction between AIIMS and Subhash Nagar
- Depot: Subhash Nagar Underpass (Jinsi)
- Number of Stations: 16
- Station Names: Karond Square, Krishi Upaj Mandi, DIG Bungalow, Sindhi Colony, Nandra Bus Stand, Bhopal Junction, Aish Bagh Crossing, Bogda Pul (interchange), Shubhash Nagar Underpass, Kendriya Vidyalaya, DB City Mall, Sangam Cinema,Rani Kamlapati Railway Station , Habibganj Naka, Alkapuri Bus Stand, AIIMS
Line-5 (Blue Line): Bhadbhada Square – Ratnagiri Tiraha
- Length: 12.91 km
- Type: Elevated
- Depot: Subhash Nagar Underpass (Jinsi)
- Number of Stations: 14
- Station Names: Bhadbhada Chauraha, Depot Chauraha, Jawahar Chowk, Roshanpura Chauraha, Kushabhau Thakre Hall, Parade Ground, Bogda Pul (interchange), Prabhat Chauraha, Govindpura, Govindpura Industrial Area, JK Road, Indrapuri, Piplani and Ratnagiri Tiraha
Proposed Routes
Line-1 (Green Line): Bairgarh – Awadhpuri
- Number of Stations: 24
- Station Names: Bairagarh, Bairagarh Stadium, Hemu Kalani, Hala Pura Bus Stand, Lal Ghati Square, Idgarh Hills, Collectorate, Cambridge School MG Hospital, Curfew Wali Mata Mandir, Kamala Park, Polytechnic Square, Roshanpura Square, TT Nagar Stadium, Mata Mandir, Jain Mandir, Sharda Mandir, Nutan College, Mansarovar Complex (Habibganj Station), Khushabhau Thakrey ISBT, Anna Nagar, Carmel Convent, Piplani Gurdwara Square, Mahatma Gandhi Square, Awadhpuri
Line-3 (Red Line): Bhauri Bypass (NH12 Junction) – Vasant Kunj Bus Stop
- Number of Stations: 24
- Station Names: Bhauri Bypass/NH12 Junction, Peepainer Village (Aerocity), Airport Road, Gandhinagar, Airport Tiraha, Manubhan Tekri, Lalghati Square, Idgarh Hills, Collectorate, Cambridge School MG Hospital, Curfew Wali Mata Mandir, Kamala Park, Polytechnic Square, Roshanpura Square, TT Nagar Stadium, Mata Mandir, Jain Mandir, Sharda Mandir, Nutan College, Mansarovar Complex (Habibganj Station), Habibganj Naka, 10 No. Square, Sai Board, Vasant Kunj Bus Stop.
Line-4 (Yellow Line): Ashok Garden Auto Stand – Mother Teresa School
- Number of Stations: 21
- Station Names: Ashok Garden Auto Stand, Krishna Campus, Railway Station, Jumerati Road, Curfew Wali Mata Mandir, Kamala Park, Polytechnic Square, Roshanpura Square, TT Nagar Stadium, Mata Mandir, MACT Square, Panchsheel Nagar Bus Stop, Ekant Park, Sahapura Lake, Bhoj University (Chunnabhatti), IIPM Sarvadham, Mansarovar School, CI Height Nayapura Bus Stop, Sanskar Marriage Garden, Bhairagarh Chichali, Mother Teresa School
Line-6 (Brown Line): Habibganj Naka – Mandideep
- Number of Stations: 12
- Station Names: Habibganj Naka, RRL, BU University, Bagsewania Bus Stop, Ashima The Lake City Mall, Sri Ram Colony, C21 Mall, Scope College (Bharopur), Regional 1 / NH-12, Harigangar Nagar, Regional 2, Mandideep.
Recent Updates:
| Launching of OWG Bridge In September 2024, RKC Infratech launched the 416 MT and 65 meters long Open Web Girder (OWG) bridge for Bhopal Metro’s priority corridor which covers 7 km distance from Subhash Nagar to Aiims through 8 stations. This development took place at Habibganj Naka across the Indian Railways’ 3 main-line tracks. Track Work Progress Of the proposed 15 km-long track (upline and downline) between Subash Nagar and AIIMS, 14 km has been successfully completed. Work on the remaining 1 km section is currently in progress. Once completed, authorities will initiate a trial run across the entire stretch. Inspection In November 2024, The Managing Director of Madhya Pradesh Metro Rail Corporation Shri S. Krishna Chaitanya conducted thorough inspection of the Bhopal Metro Priority Corridor section from Subhash Nagar Station to Rani Kamlapati Metro Station. |

Benefits of Bhopal Metro
Enhanced Connectivity: A metro system in Bhopal will increase the connectivity in the city by connecting key areas like educational and medical institutions, workplaces and commercial centers through a more convenient mode of transport. This enhanced connectivity will facilitate the residents of the city to commute to different areas of the city more efficiently and in less time.
Reduced Traffic Congestion: Due to rapid urbanisation and increasing population the city is witnessing major traffic congestion on the roads. A metro system will provide the residents of the city with a fast and efficient mode of transport as compared to private vehicles which will alleviate the traffic congestion on the roads of Bhopal.
Economic Growth: The construction and operation of a metro system in Bhopal will create several job opportunities in the city and will attract more business setups and investments near the metro stations which will encourage the local economy and promote economic growth of the city.
Environmental Benefits: The Bhopal Metro project will promote a more sustainable and environmentally friendly mode of transportation in the city. A metro system will provide the residents with a reliable alternative to road transport which will lower the emission of pollutants such as carbon dioxide from vehicles reducing air pollution in the city.
Challenges In Bhopal Metro
Ridership Concern: The ridership level is a primary challenge before the establishment of any metro project. For Instance, the Pune Metro is currently facing a shortfall in the daily ridership level with only 150,000 passengers compared to a projected figure of over 600,000 for 2021. The financial viability of any metro project depends on its ridership level. Hence, achieving project ridership is very important to make any project successful and sustainable for a long period of time.
Financial Constraints: Securing adequate funding for the Bhopal Metro project is critical for the MPMRCL. The delay in fund allocation can hinder the progress of the project and also increase its cost.
Integration with other modes of Transport: Integrating the Bhopal metro with the existing modes of transport like buses and rickshaws is a major challenge. To make the project successful it is very important to link the metro system with other modes of transport which will allow passengers to switch to different modes of transportation smoothly.
Encroachment Issues: The authorities have identified encroachment issues along the planned Bhopal metro development routes, particularly near main roads in areas like Jinsi and Karond. These issues can potentially impact the deadline of the project.
Conclusion
The Bhopal Metro project, implemented by Madhya Pradesh Metro Rail Corporation Limited is a notable step towards streamlining the connectivity in the state capital. With 2 corridors under construction of 6, Bhopal Metro is set to cater to over 2.20 lakh daily commuters, addressing the city’s growing demand for efficient public transport. However, the project is running behind its original deadline of commencing operation on the priority corridor due to some critical challenges. While Bhopal Metro has the potential to set a benchmark for urban mobility in smaller cities, its success will depend on careful attention to operational efficiency, ridership engagement, and integration with the city’s broader development goals.







