Introduction
As India steps into 2026, it becomes essential to take a measured view of the cumulative progress that has been achieved across the country’s rail mobility landscape. Over the past year, rail development has moved beyond a narrow focus on route additions and project commissioning. Instead, the emphasis has increasingly shifted towards building integrated, technology-driven, and resilient systems capable of supporting India’s long-term urbanisation and economic growth.
This transition is visible in the growing adoption of advanced signalling and rolling stock technologies, the steady expansion of indigenisation across critical rail systems, and sustained efforts to increase safety, reliability, and operational efficiency. Together, these developments reflect a broader attempt to strengthen rail mobility as a core component of national infrastructure and a key enabler of a Viksit and Atmanirbhar Bharat.
During 2025, multiple segments of India’s rail ecosystem recorded notable milestones. The continued expansion of Vande Bharat train services improved intercity connectivity across key corridors, while the approval of new RRTS corridors recognises the role of high-frequency regional rail in addressing emerging mobility demands. At the urban level, India’s metro network crossed the 1,000-km operational mark, which shows the scale at which metro systems are now being planned, executed, and integrated into city transport frameworks.
Against this backdrop, this article presents a comprehensive overview of progress across the metro, RRTS, Indian Railways, and the country’s bullet train project. It examines key expansions, commissioning milestones, and policy developments, while reflecting on how these initiatives collectively contribute to the development of a modern, rail infrastructure capable of supporting India’s mobility needs in the decades ahead.
Indian Railways: Transitioning Towards a Safer, Faster, and Smarter Network
Railways has trancended its role of just connecting the disconnected. Today, it is striving to reposition itself as a modern mobility provider that prioritises safety, speed, and service reliability. This vision is being brought to reality with innovations, Sustainability & indigenisation. In 2025, a total of 42 railway projects were dedicated to the nation, 13 projects were inaugurated, and 21 had their foundation stones laid, with a combined estimated cost of over ₹25,000 crore.
The following sections highlight some of the key milestones achieved by Indian Railways during 2025.
Landmark Projects Commissioned:
During 2025, Indian Railways commissioned several infrastructure projects of national importance. One of the most notable developments was the commissioning of the Udhampur-Srinagar-Baramulla Rail Link (USBRL), which established rail connectivity to the Kashmir Valley. The year also saw the opening of India’s first vertical-lift railway sea bridge at Pamban, improving connectivity to Rameswaram. In the Northeast, the commissioning of the Bairabi-Sairang line extended rail access into Mizoram, strengthening regional connectivity.
- Connecting the Kashmir Valley with the Nation: Commissioning of USBRL Project:
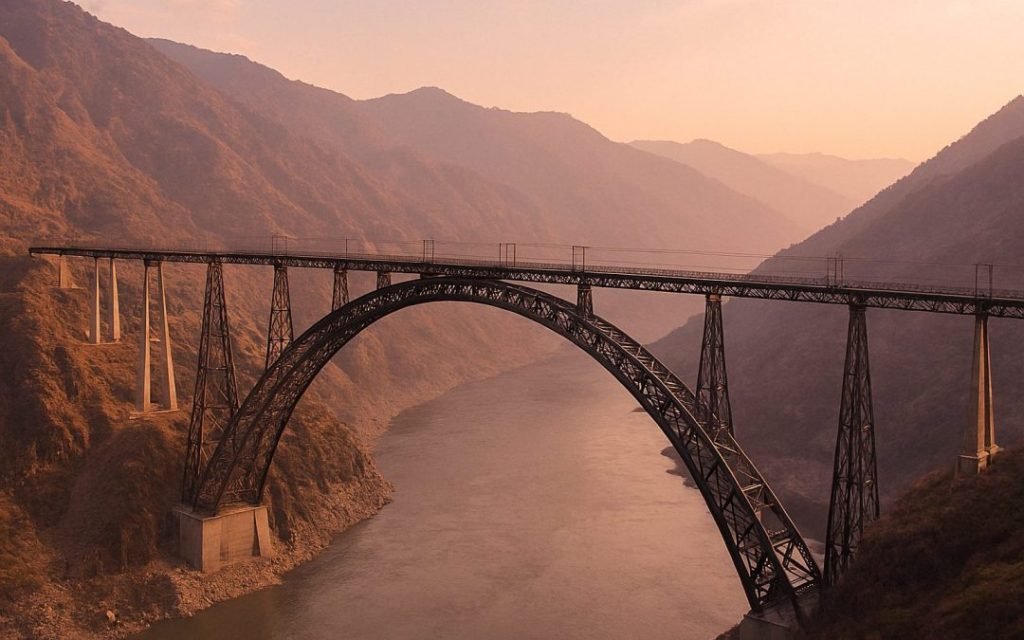
The Udhampur-Srinagar-Baramulla Rail Link project carries profound national significance; it was a dream that was finally realised after 100 years in 2025. With the commissioning of this 272 km rail link, Kashmir is again engraved on the map of Indian Railways. Beyond connectivity, the USBRL project highlights India’s engineering prowess in executing complex infrastructure projects in some of the country’s most challenging geographies. The project features 3 landmark structures, including:
- The world’s highest railway arch bridge, the Chenab Bridge
- India’s first cable-stayed railway bridge, the Anji Bridge
- India’s longest operational railway tunnel, T-50.
By connecting more than 95 villages, the USBRL project is expected to provide reliable, all-weather transportation and play a catalytic role in facilitating regional development. Improved accessibility is anticipated to support employment generation, tourism, education, and broader economic activity.

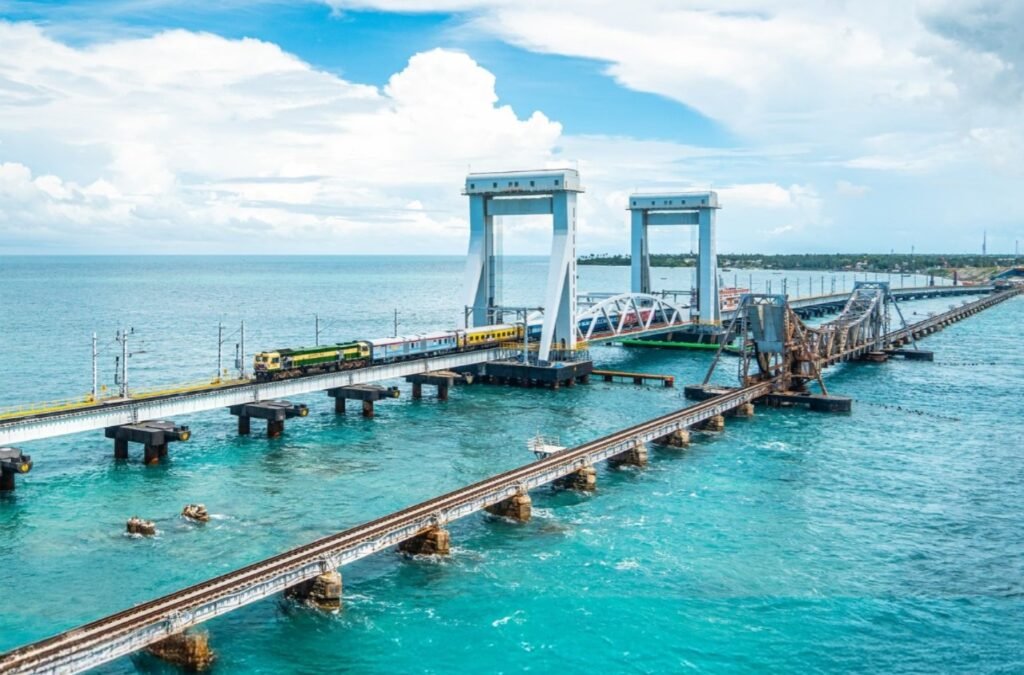
- India’s First Vertical-Lift Railway Sea Bridge
Another achievement was the inauguration of the New Pamban Bridge on 6 April 2025. This bridge is India’s first vertical-lift railway sea bridge. It connects Rameswaram to the Indian mainland and has a projected design life of over 100 years. The bridge restores a vital rail link to Rameswaram. Beyond local travel, the bridge also supports pilgrimage and tourism while opening possibilities for future transport links across the Palk Strait between India and Sri Lanka.

- North East Rail Link: Bairabi-Sairang Line
In 2025, Indian Railways improved connectivity in the Northeast with the inauguration of the 51 km Bairabi-Sairang broad-gauge line in Mizoram. This line places Aizawl on India’s rail map for the first time.

New Economic Corridors
In 2025, Indian Railways continued its efforts to improve capacity, efficiency, and sustainability. Beyond moving passengers, the IR is working toward stimulating economic activity, with dedicated freight corridors.
Three Major Economic Corridors
Under three identified economic corridors, a total of 434 projects have been planned with a combined estimated cost of ₹11.17 lakh crore:
- Energy, Mineral & Cement Corridor: 192 projects
- High-Traffic Density Routes: 200 projects
- Port Connectivity: 42 projects
So far, 121 of the 434 identified projects have been approved, covering a track length of 12,133 km with a total estimated cost of ₹2,02,551 crore.
By improving freight efficiency and linking industrial hubs with ports and consumption centers, these corridors are expected to strengthen regional economies, support supply chains, and lay the groundwork for future industrial and logistics growth.
Indian Railway Rises as World’s 2nd Largest Freight Carrier
In 2025, India strengthened its position on the global rail freight map, overtaking both the United States and Russia to become the world’s 2nd-largest rail freight carrier. Over the 2024–25 financial year, Indian Railways moved 1.6 billion metric tonnes of goods, a milestone largely enabled by the Eastern and Western Dedicated Freight Corridors. This growth is not just a reflection of volume; it signals a broader shift toward a freight system that is more efficient, cost-effective, and environmentally sustainable, supporting the country’s industrial and economic development.

Wagon Production Ramps Up as Freight Volumes Rise
Indian Railways has scaled up wagon production as part of its broader effort to strengthen freight operations and improve earnings. This push aligns with the long-term objective of achieving 3,000 million tonnes of freight loading by 2029–30, which requires a sustained increase in wagon availability. The upward trend has continued in the current year, with 33,703 wagons produced between January and November 2025, indicating consistent improvement in wagon supply.
Modernising the Passenger Fleet Through LHB Coach Production
Indian Railways has continued to expand the indigenous production of LHB coaches as part of its ongoing coach modernisation programme. This effort supports the broader objectives of Atmanirbhar Bharat and Make in India, while also improving safety and ride quality across the passenger fleet.
In FY 2025–26 (up to November 2025), more than 4,224 LHB coaches were produced, which signals an 18% increase over the corresponding period of the previous year.
Production details:
- ICF Chennai: 1,659 coaches
- MCF Raebareli: 1,234 coaches
- RCF Kapurthala: 1,331 coaches
Strengthening India’s Self-Reliance in Locomotive Manufacturing
Indian Railways has expanded domestic locomotive manufacturing to enhance haulage capacity and reduce import dependence. Between January and November 2025, a total of 1,542 electric locomotives were produced. This growth is supported by modern manufacturing facilities developed through public-private partnership (PPP) models.
Madhepura Electric Locomotive Factory (Bihar)
The facility is part of the partnership between Indian Railway and Alstom India. The facility has supplied 576 units of 12,000 HP electric locomotives, including 76 units, from April to November 2025.

Marhowra Diesel Locomotive Factory (Bihar)Set up in partnership with Wabtec Locomotive Private Limited, the factory has delivered 773 locomotives so far (569 of 4,500 HP and 204 of 6,000 HP), including 73 units in FY 2025–26 (up to November). About 65% of components are sourced domestically. The facility has also secured USD 400 million export orders for 150 locomotives to Guinea.
Dahod Electric Freight Locomotive Facility (Gujarat)
In response to meet the freight demand, Indian Railways has partnered with Siemens Mobility, which is set to deliver 1,200 Electric Locomotives of 9000 HP and provide 35 years of full-service maintenance. The production will take place at the Dahod facility, which was inaugurated by Prime Minister Narendra Modi on May 26, 2025.

Electrification on Track
Sustainability has become a central operational priority for Indian Railways. As part of its objective to achieve net-zero emissions by 2030, the focus on electrification has been accelerated across the network. As of now, about 99.2% of the Broad Gauge network has been electrified, with work underway on the remaining sections.

This level of electrification places Indian Railways ahead of several major rail networks globally, including the UK, Russia, and China. At the domestic level, 14 Railway Zones and 25 States and Union Territories have already achieved 100% electrification.
Track Infrastructure Expansion
Network capacity enhancement has continued to remain a focus area for Indian Railways. Between 1 April and 30 November 2025, more than 900 km of new railway lines were commissioned.
Alongside new line additions, track renewal has progressed at scale. During the same period, rails were renewed over 6,880 track kilometres. This augmentation continues to improve ride quality, higher permissible speeds, and enhanced safety across the network.
Indian Railways’ Steady Shift towards Safer Operations
Technology-led interventions are strengthening the safety framework of Indian Railways. In this context, Kavach emerges as a central element of this shift. The indigenously developed Automatic Train Protection (ATP) system enforces speed limits and initiates automatic braking in cases of human error. In 2025, Kavach Version 4.0 has been commissioned over 738 route kilometres and is slated for wider deployment across the network as part of a long-term safety strategy.
These efforts are supported by a substantial rise in financial commitment. The safety budget has nearly tripled over the past decade, increasing from ₹39,463 crore in FY 2013–14 to ₹1,16,470 crore in the current financial year.
The Amrit Bharat Station Scheme: A Nationwide Push to Modernise Railway Stations
The Amrit Bharat Station Scheme has initiated a large-scale transformation of passenger railway stations across the country. The programme moves beyond the conventional view of stations as mere transit points. Today, the stations are being seen as integrated urban spaces that connect transport with the surrounding city.
Under the scheme, 1,337 stations have been identified for redevelopment, making it one of the largest station reconstruction initiatives globally. As of December 2025, redevelopment has been completed at 155 stations, with construction activity continuing at many others at different stages of progress.
Green Railway Stations: A Big Step Towards Net-Zero Emissions
Indian Railways is pursuing a range of measures to move towards net zero emissions, with a growing focus on integrating renewable energy into its operations. Solar power has become a key component of this transition, with around 2,626 railway stations across the country now powered by solar energy.
In parallel, Indian Railways has commissioned a total of 898 MW of solar power capacity, of which nearly 70% is being used for traction. This shift has helped improve energy security and lower carbon emissions while supporting more environmentally responsible railway operations.
Expansion of New-Generation Passenger Train Services
- Vande Bharat Train: By 26 December 2025, the Vande Bharat programme had expanded to 164 train services across the Indian Railways network, which reflects its nationwide acceptance and operational maturity. During the calendar year 2025 alone, 15 new Vande Bharat Express services were introduced.
- Amrit Bharat trains are non-AC services introduced to improve travel conditions for passengers who rely on sleeper and general class coaches. In 2025, 13 Amrit Bharat Express services were added. With these additions, 30 Amrit Bharat trains are now running on the Indian Railways network.
The progress recorded over the past year reflects Indian Railways’ steady efforts to strengthen its role in national development. The focus has extended beyond expanding routes to improving operational efficiency, safety standards, and service quality. Through sustained investment and system-level reforms, the rail network continues to support economic activity while responding to the growing demand for reliable and sustainable mobility. Railways has historically played a central role in India’s growth, and recent developments reaffirm its relevance in a changing transport landscape.
India’s Metro Revolution
Much like the national rail network, India’s metro rail systems have emerged as a critical component of urban mobility. What began as a solution for a few large cities has gradually evolved into a reliable and widely accepted mode of transport for dense urban regions. As congestion intensifies and emissions rise due to increasing dependence on private vehicles, metro rail has proven its ability to move large passenger volumes efficiently while limiting environmental impact.
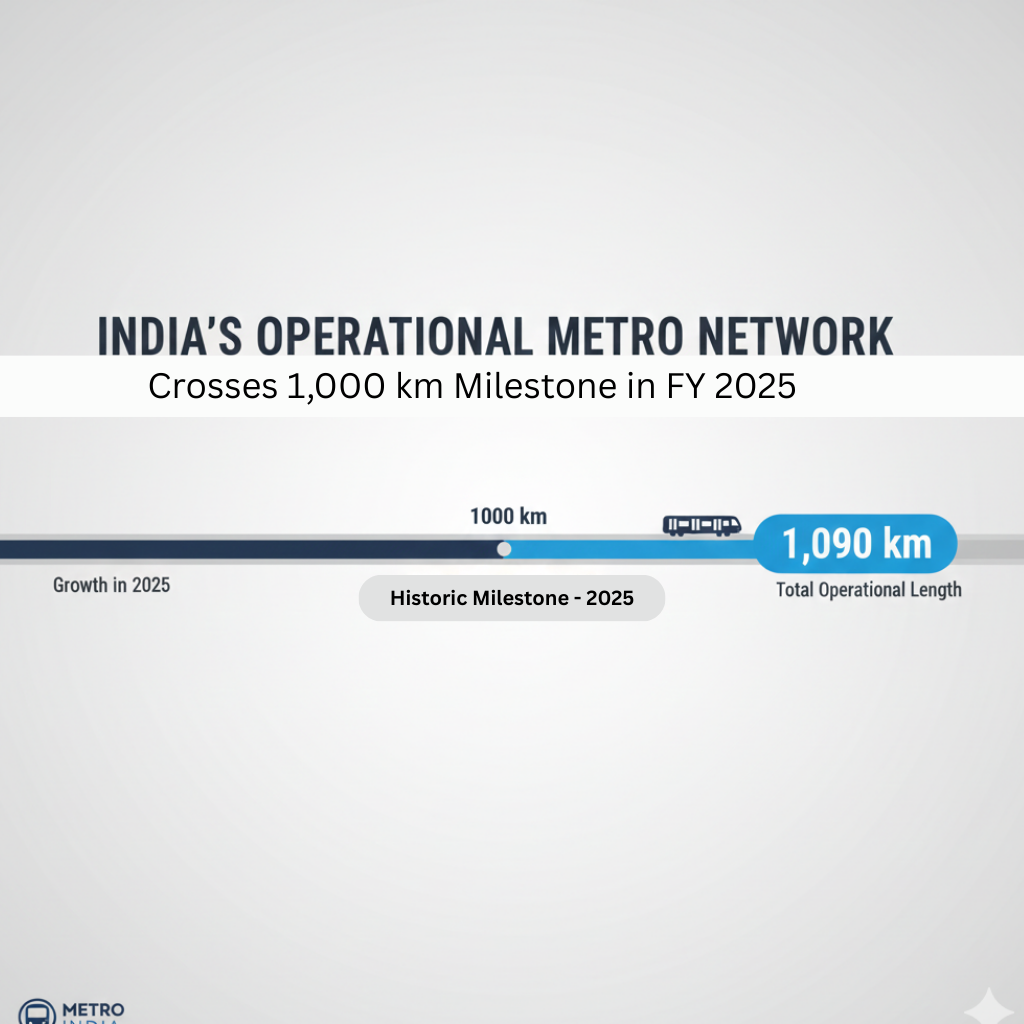
By 2025, India’s operational metro network crossed the 1,000 km mark, placing the country among those with the largest metro systems globally. Alongside this growth, several cities are planning new metro projects, while existing networks continue to expand toward suburban and peripheral areas to improve regional connectivity.
The scale and pace of this expansion during 2025 are reflected in the following key indicators.
Operational Metro Network in India
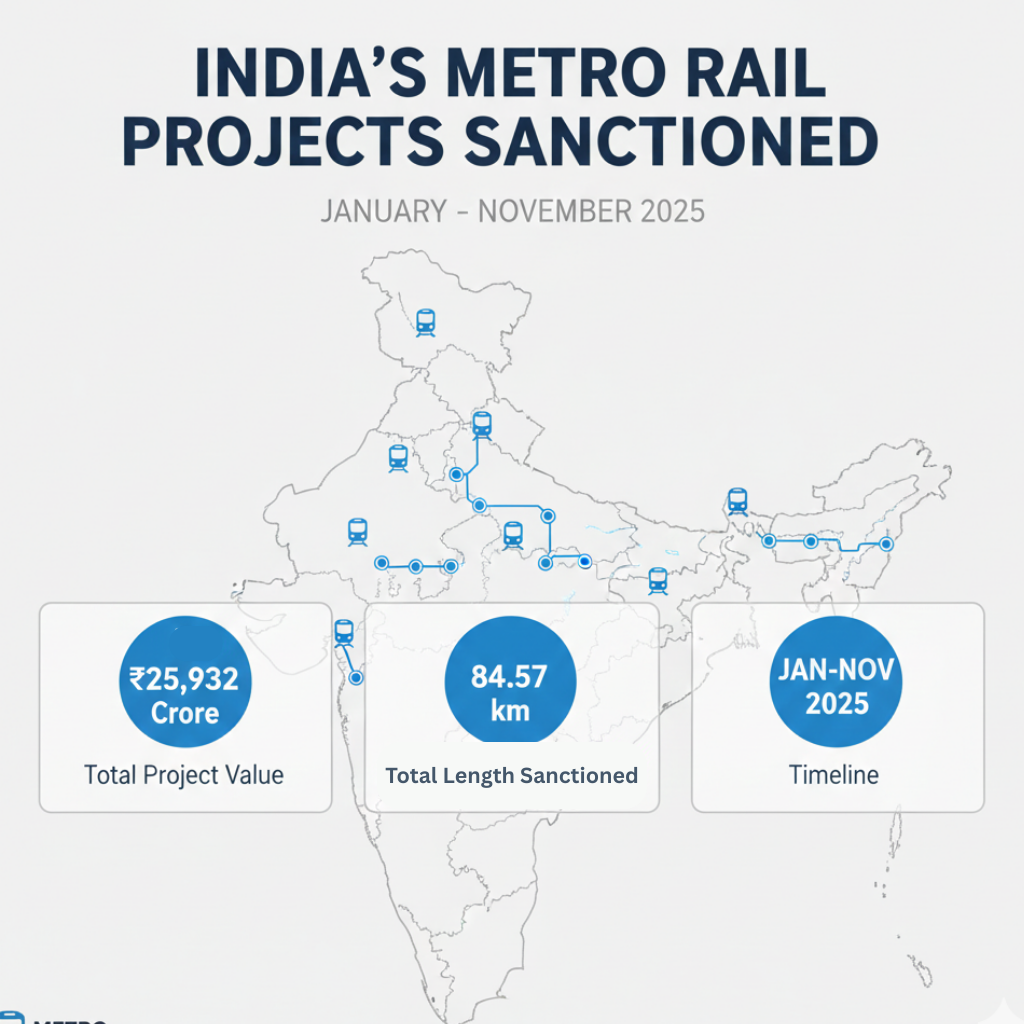
Metro Rail Projects Sanctioned between January and November 2025
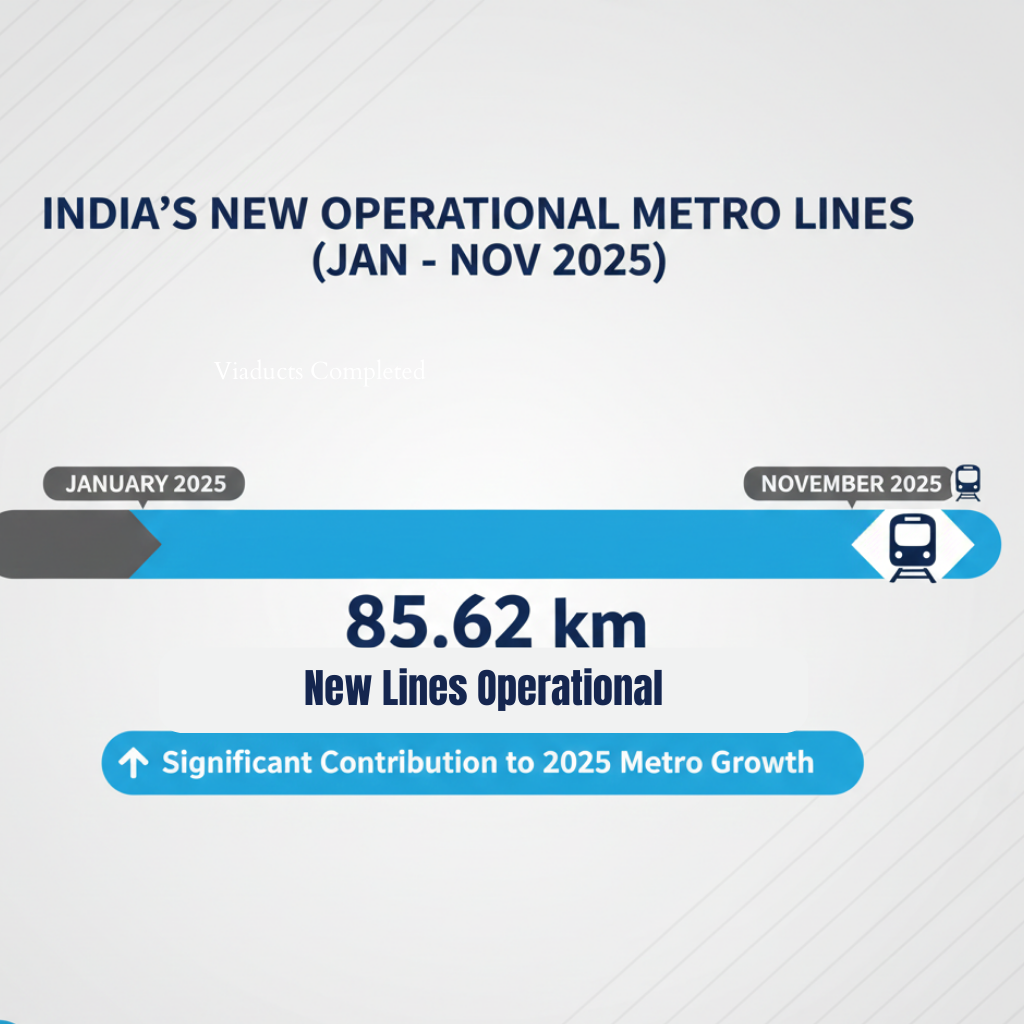
New Metro Lines Commissioned in 2025
Expansion of Metro Services Across Cities
Key Operational Milestones in 2025
Opening of 1st Section of Delhi Metro Phase 4
Delhi Metro’s Phase IV programme moved from planning to operations in January 2025 with the opening of its first completed section. During the year, a 2.8-km stretch between Janakpuri and Krishna Park was inaugurated. The section signals the start of the next phase of network expansion in Delhi.

Rithala-Kundli Expansion
Alongside the commissioning of the first Phase IV section, progress was also made on future corridors under Delhi Metro’s expansion programme. During the year, the foundation stone was laid for the 26.5-km Rithala-Kundli corridor. The corridor will extend metro connectivity from Rithala in Delhi to Nathupur in Kundl.
Expansion of Ahmedabad Metro Phase 2 Services
Ahmedabad Metro Phase II is being developed as an extension of Phase I to strengthen connectivity between Ahmedabad and Gandhinagar. A major portion of the corridor became operational in September 2024, when 20.8 km of the 28.2-km alignment, along with 8 hstations covering the Motera-Mahatma Mandir and GNLU-GIFT City sections, was inaugurated in 2024. A 1.9 km route up to Sachivalaya was commissioned for passengers in April 2025.
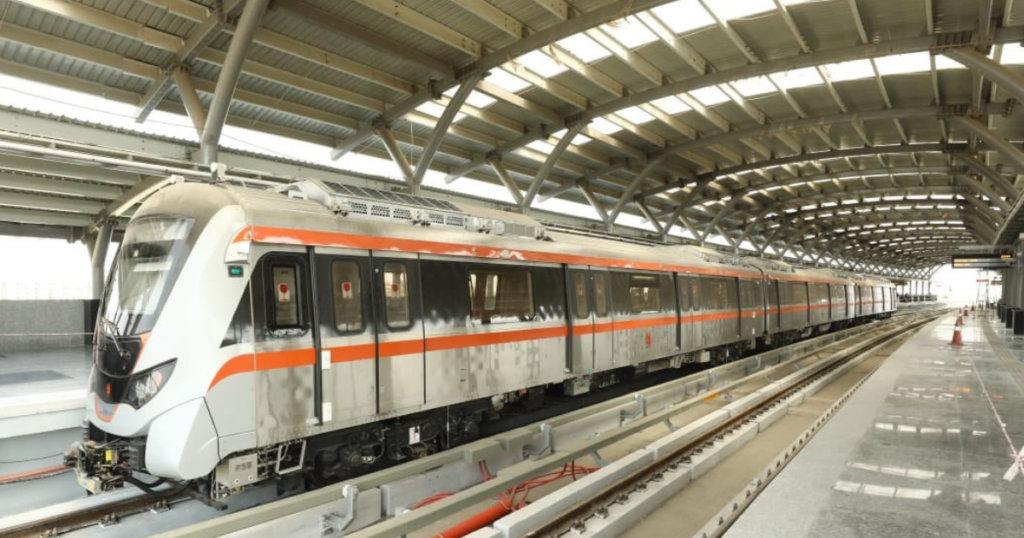

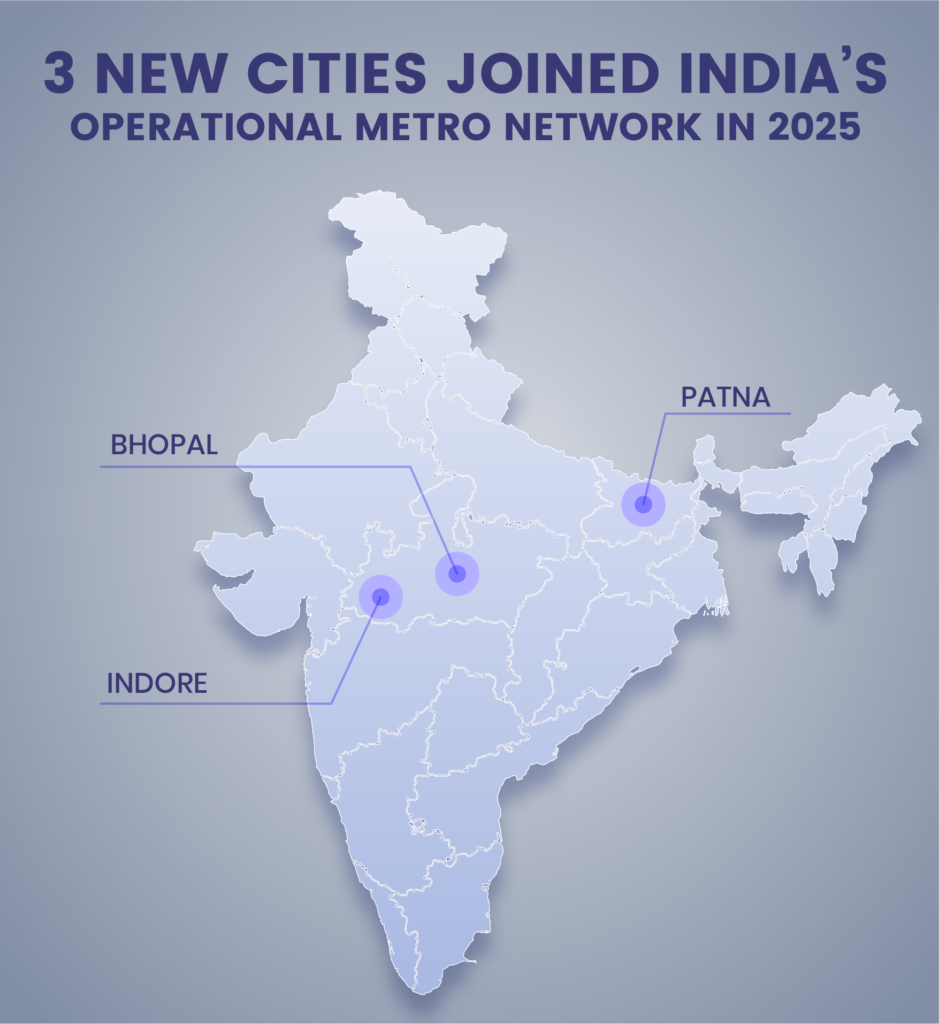
Indore Joined India’s Metro Network
Indore made its debut into India’s metro network in 2025 with the inauguration of the first phase of its Yellow Line. The initial section, designated as the Super Priority Corridor, was opened to passengers on 31 May 2025, which made metro rail services available to the city for the first time.
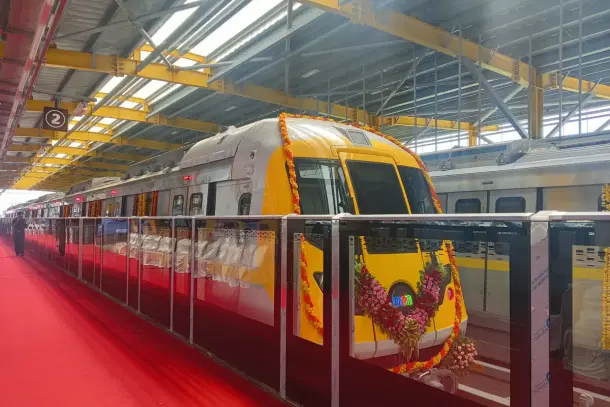

India’s Oldest Metro Continues to Expand
India’s oldest metro system continued to expand in 2025 with the opening of new sections across the Green Line, Orange Line, and Yellow Line. These were all officially inaugurated on August 22, 2025.
The newly operational sections in 2025 are:
| Line | Section | Length |
| Green Line | Sealdah-Esplanade | 2.6km |
| Yellow Line | Nopara-Jai Hind Bimanbandar | 6.7km |
| Orange Line | Hemanta Mukhopadhyay- Beleghata | 4km |
Inauguration of Bengaluru Metro Yellow Line
Bengaluru’s metro network continued to expand in 2025, which reflects the city’s growing reliance on rail-based urban transport. A key development during the year was the opening of the 19-km Yellow Line between RV Road and Bommasandra in August, adding an important north-south link to the system. The corridor has taken Bengaluru’s operational metro length to 96 km.
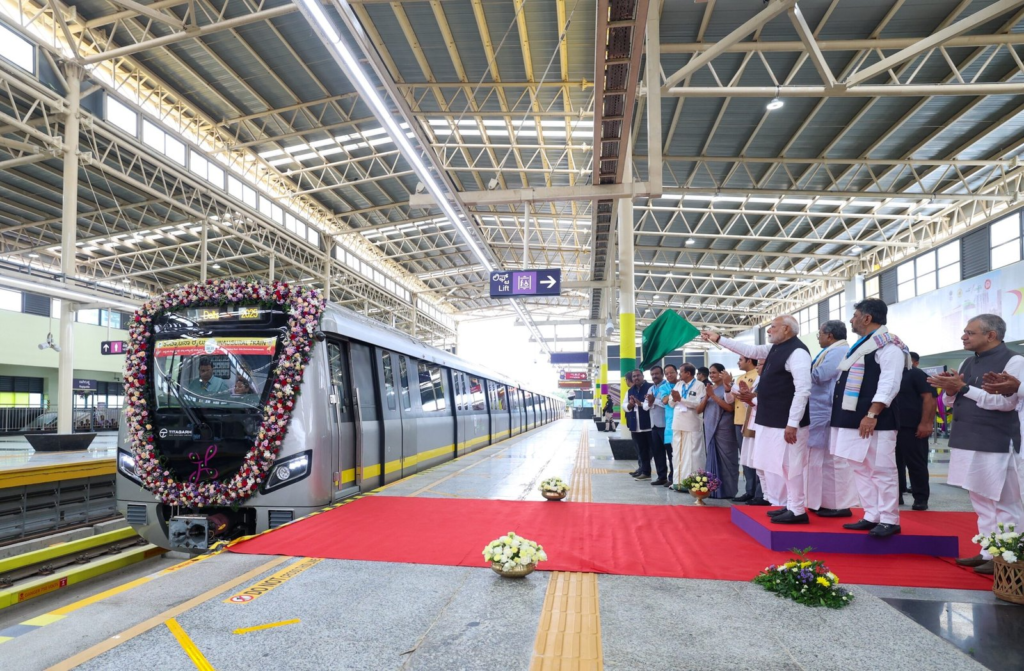

Foundation Stone of Phase 3
Alongside this operational milestone, the city also moved into its next phase of expansion. The foundation stone for Bengaluru Metro Phase 3 was laid during the year, which signals the start of a ₹15,610-crore programme that will add more than 44 km of new lines with 31 elevated stations. Once completed, Phase 3 is expected to extend metro coverage to new growth areas and strengthen the overall reach of the network.

Mumbai’s Aqua Line Became Fully Operational
After years of construction and testing, one of India’s most complex metro projects, Mumbai Metro Line 3, became operational in October 2025. As the city’s first fully underground metro corridor, the 33.5-km line now provides end-to-end connectivity from Aarey JVLR to Cuffe Parade via BKC. Since commissioning, the corridor has begun to show its impact on urban travel patterns, recording a peak daily ridership of about 1.8 lakh passengers, with average daily ridership stabilising around 1.4 lakh.

Metro Services Commenced in Patna
Patna entered India’s metro map in 2025 with the partial commissioning of its first corridor. On 6 October 2025, operations began on the 3.6-km Priority Corridor of the Blue Line, connecting New ISBT, Zero Mile, and Bhootnath stations.
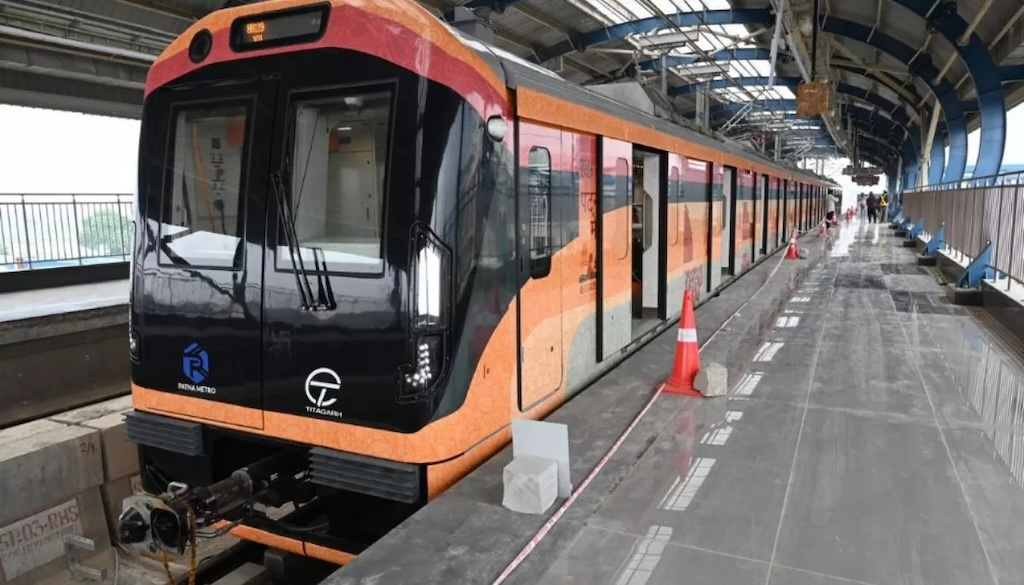

Bhopal entered India’s Metro Club
Bhopal became part of India’s metro system in December 2025 with the formal inauguration of the Bhopal Metro, also known as the Bhoj Metro. The commercial operations began on 21 December 2025 on the stretch between Subhash Nagar and AIIMS Bhopal.
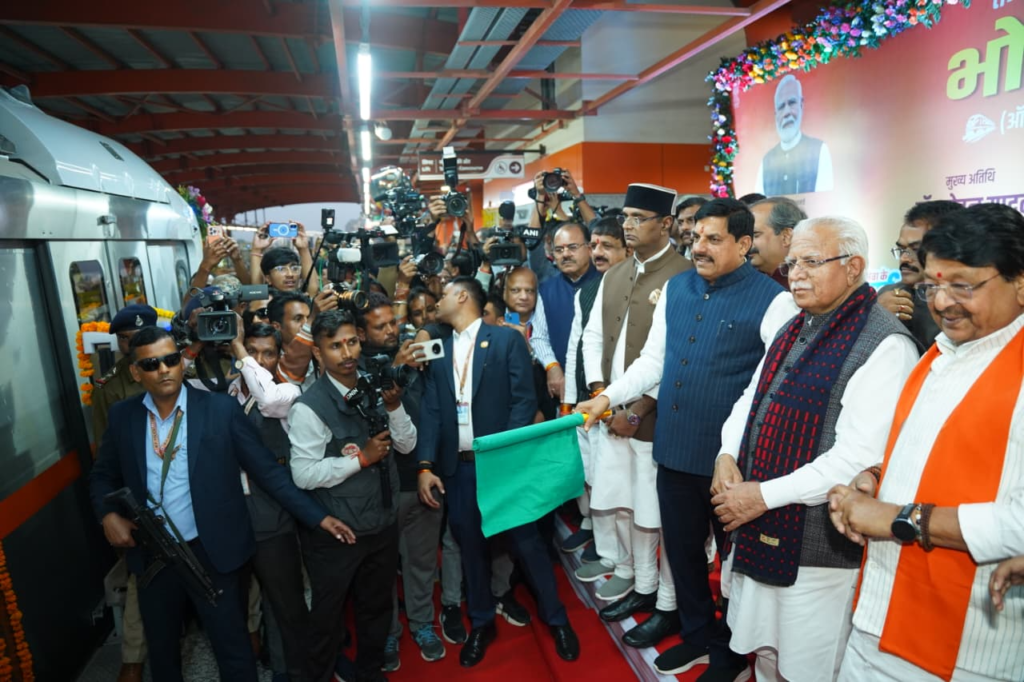

The year 2025 proved to be a crucial period for India’s metro sector. Metro services were extended to 3 new cities, while network expansion continued across several existing systems. At the same time, new metro projects progressed in cities such as Visakhapatnam and Vijayawada, which shows a sustained momentum in urban rail development across the country.
Progress on India’s RRTS Network
The Delhi-Meerut RRTS Line, also known as the Namo Bharat Corridor acheived expansion and ridership milestones in 2025. It has extended its reach into Delhi.
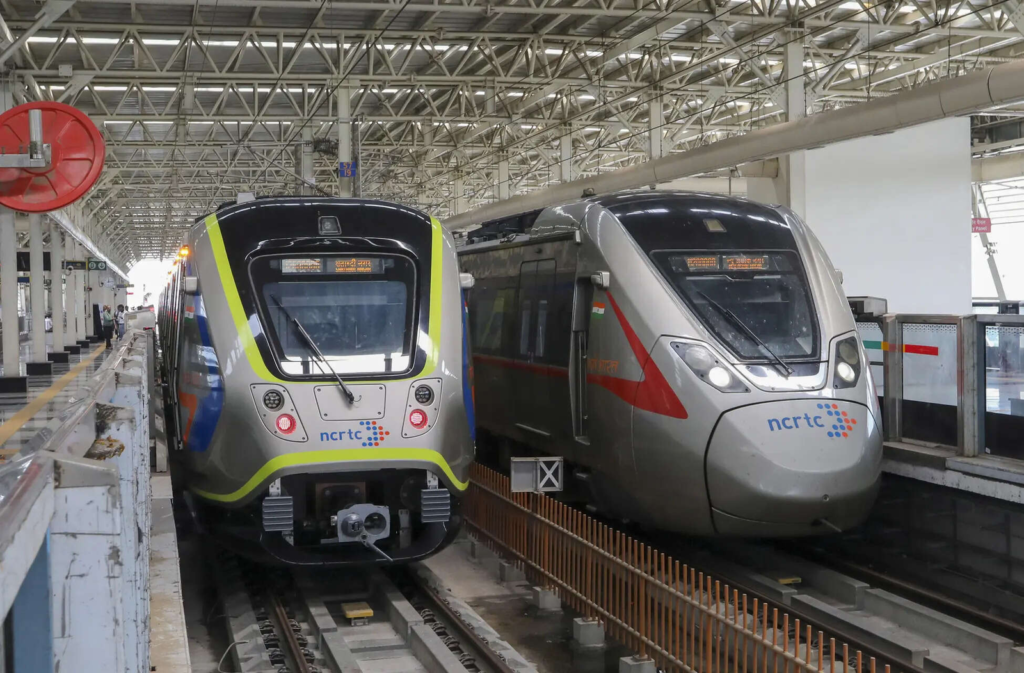

1. Network Expansion
- Entry into Delhi (Jan 5, 2025): Prime Minister Narendra Modi inaugurated a 13-km extension from Sahibabad to New Ashok Nagar. This brought the total operational length to 55 km with 11 functional stations.
- Operational Stretch: As of now, the corridor provides semi-high-speed connectivity spanning 55km from New Ashok Nagar (Delhi) to Meerut South (UP).
2. Ridership and Performance Milestones
- 2 Crore Commuter Trips: By December 2025, the Namo Bharat RRTS surpassed a cumulative 20 million passenger journeys since its October 2023 launch.
- Ridership Surge: Monthly footfall peaked at nearly 15 lakh commuters by mid-2025, with single-day ridership records exceeding 81,500 passengers.
3. Awards and Sustainability
Global Recognition: NCRTC was conferred with the UITP Award 2025 for Public and Urban Transportation Strategy, along with the Gold Award at the National Awards for e-Governance 2025.

Green Energy: On the sustainability front, NCRTC launched a pilot ‘Solar on Track’ initiative at the Duhai Depot and secured a Platinum rating for the Anand Vihar underground station from the Indian Green Building Council.
PIB Sanctions 2 New RRTS Lines for NCR
In November 2025, the Public Investment Board (PIB) approved two new Regional Rapid Transit System (RRTS) corridors for the National Capital Region (NCR). The new RRTS lines are:
| RRTS Line | Length | Estimated Cost |
| Sarai Kale Khan-Bawal | 93km | Rs 320bn |
| Sarai Kale Khan- Karnal | 136km | Rs 330bn |
High-Speed Rail Development in India
India’s first bullet train project has started taking shape. The 508 km-long high-speed rail corridor will connect Mumbai and Ahmedabad through 12 stations. The first section of this corridor is expected to be operational by mid-2027.
- Project Progress Overview
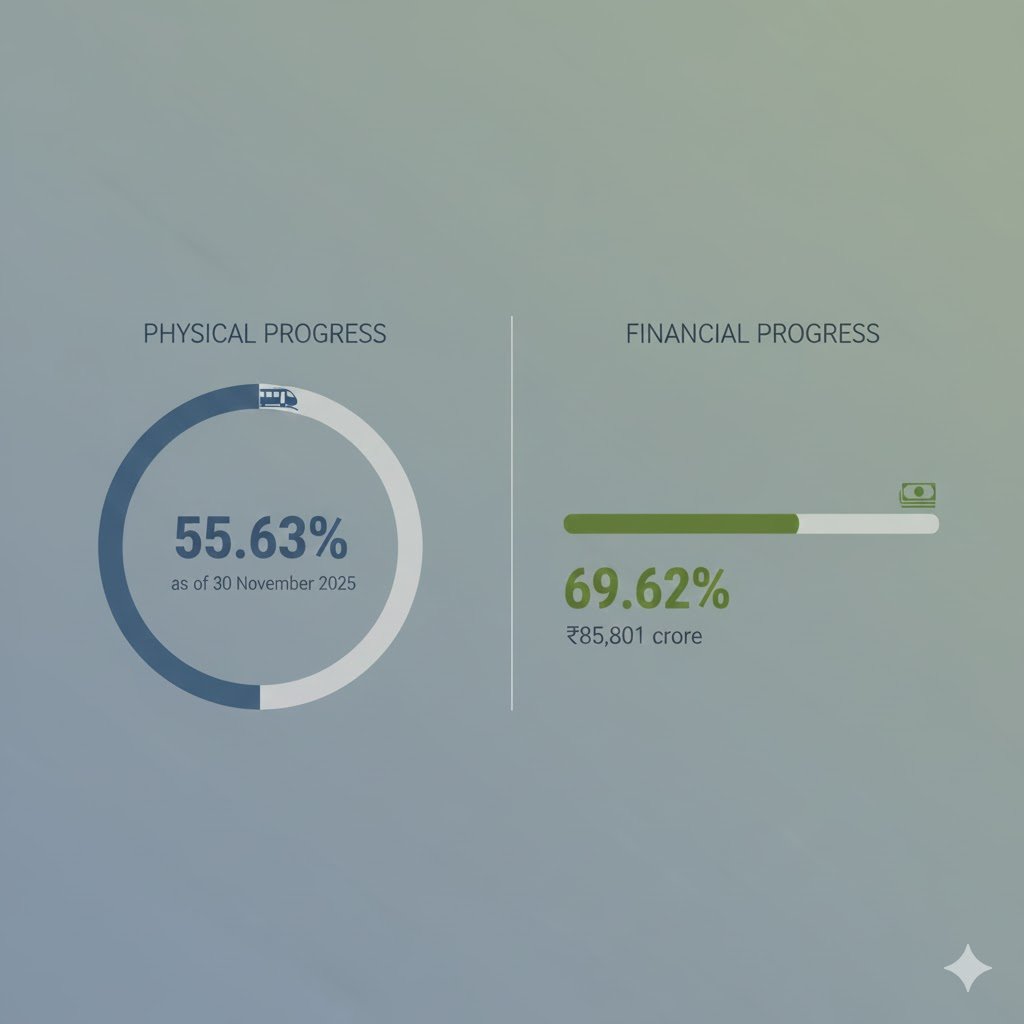
Construction Progress

Bridges & Structures Completion

Milestones Completed in 2025
- Completion of First Underground Tunnel
In September 2025, the bullet train project reached a crucial milestone with the completion of the 4.88 km undersea tunnel connecting Ghansoli and Shilphata. This achievement signaled the successful conclusion of one of the most challenging sections of the alignment.
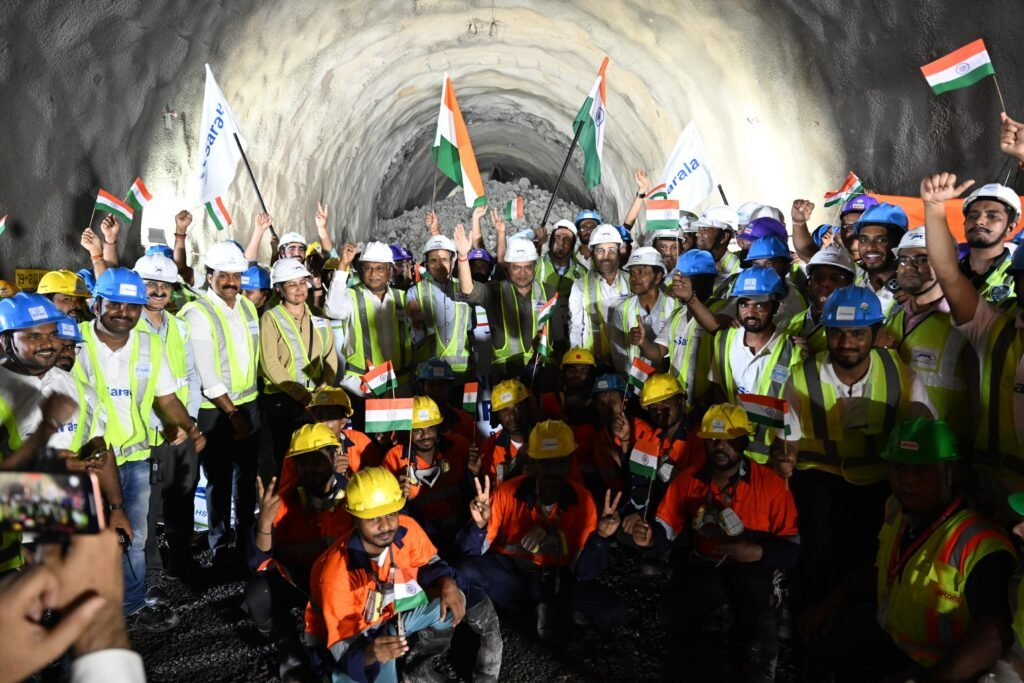

Mountain Tunnel Breakthrough
The first mountain tunnel breakthrough was achieved in the nearly 1.5-kilometer-long Mountain Tunnel-5 (MT-5) in the Palghar district of Maharashtra.
Construction Progresses on 7 Mountain Tunnels in Maharashtra
| Tunnel ID | Length (metres) | Current Status / Progress |
| MT-1 | 820 | 15% completed |
| MT-2 | 228 | Preparatory works underway |
| MT-3 | 1,403 | 35.5% completed |
| MT-4 | 1,260 | 31% completed |
| MT-6 | 454 | 35% completed |
| MT-7 | 417 | 28% completed |
| Total | 6,000 | Seven mountain tunnels under construction |
This progress reflects the steady momentum of India’s first bullet train project towards completion. Despite earlier delays, the project has continued to maintain its pace. According to Railway Minister Ashwini Vaishnaw, the first section will open between Surat and Bilimora in Gujarat in 2027, followed by two more sections Vapi to Surat and Vapi to Ahmedabad.
Conclusion
As India moves into 2026, the developments of the past year point to a gradual but clear evolution in the country’s rail mobility framework. The focus is no longer limited to adding new routes or announcing projects, but to strengthening systems, improving safety, and ensuring that investments translate into reliable and efficient operations. Progress across Indian Railways, metro networks, RRTS corridors, and the high-speed rail project reflects this shift towards integration, capacity building, and long-term sustainability. The advancements in indigenisation, electrification, station redevelopment, and modern rolling stock indicate a more structured approach to meeting growing mobility demands. At the same time, the expansion of metro and regional rail services into new cities highlights the increasing role of rail-based transport in urban and regional planning. While execution challenges will continue to test institutions, the direction taken during 2025 suggests a more mature and outcome-oriented rail ecosystem that is well established to support economic activity, urban growth, and environmental goals in the years ahead.
Discover how AI is bringing the next phase of sustainable urban rail mobility for Viksit Bharat at InnoMetro 2026, India’s prime exhibition and conference for metro & railways which is going to take place on 21-22 May 2026 at Bharat Mandapam, New Delhi
Register now: https://innometro.com/visitor-registration/








